EMMA: Extensible MultiModal Annotation
markup language
- This version:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2005/WD-emma-20050916/
- Latest version:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/
- Previous version:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/WD-emma-20041214/
- Editor in chief:
- Michael Johnston, AT&T
- Editors:
- Wu Chou, Avaya
- Deborah A. Dahl, Independent Consultant
- Gerry McCobb, IBM
- Dave Raggett, W3C/Canon
Copyright
© 2005 W3C ®
(MIT ,
ERCIM,
Keio), All Rights Reserved.
W3C liability,
trademark,
document
use rules apply.
Abstract
The W3C Multimodal Interaction working group aims to develop
specifications to enable access to the Web using multimodal
interaction. This document is part of a set of specifications for
multimodal systems, and provides details of an XML markup language
for containing and annotating the interpretation of user input. Examples of
interpretation of user input are a transcription into words of a
raw signal, for instance derived from speech, pen or keystroke
input, a set of attribute/value pairs describing their meaning, or
a set of attribute/value pairs describing a gesture. The
interpretation of the user's input is expected to be generated by
signal interpretation processes, such as speech and ink
recognition, semantic interpreters, and other types of processors
for use by components that act on the user's inputs such as
interaction managers.
Status of this Document
This section describes the status of this document at the
time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this
document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest
revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at
http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This document is a W3C Last Call Working Draft for review by W3C members
and other interested parties. Publication as a Working Draft does
not imply endorsement by the W3C Membership. This is a draft
document and may be updated, replaced or obsoleted by other
documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this document as
other than work in progress.
This specification describes markup for representing
interpretations of user input (speech, keystrokes, pen input etc.)
together with annotations for confidence scores, timestamps, input
medium etc., and forms part of the proposals for the W3C Multimodal Interaction
Framework.
This document has been produced as part of the W3C Multimodal Interaction
Activity, following the
procedures set out for the W3C Process, with the
intention of advancing it along the W3C Recommendation track. The
authors of this document are members of the W3C Multimodal Interaction
Working Group (members
only).
This document was produced under the
5
February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. The Working Group maintains
a public list
of patent disclosures relevant to this document; that page also
includes instructions for disclosing [and excluding] a patent. An
individual who has actual knowledge of a patent which the individual
believes contains Essential Claim(s) with respect to this specification
should disclose the information in accordance with
section 6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
Your feedback is welcomed. Comments on this document are due
28 October 2005; please send them to the public mailing list:
www-multimodal@w3.org
(public
archives). See W3C mailing
list and archive usage guidelines.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Structure of EMMA documents
- 3. EMMA structural elements
- 4 EMMA annotations
- 4.1 EMMA annotation elements
- 4.2 EMMA annotation attributes
- 4.2.1 Tokens of input:
emma:tokens attribute
- 4.2.2 Reference to processing:
emma:process attribute
- 4.2.3 Lack of input:
emma:no-input attribute
- 4.2.4 Uninterpretable input:
emma:uninterpreted attribute
- 4.2.5 Human language of input:
emma:lang attribute
- 4.2.6 Reference to signal:
emma:signal attribute
- 4.2.7 Media type:
emma:media-type attribute
- 4.2.8 Confidence scores:
emma:confidence attribute
- 4.2.9 Input source:
emma:source attribute
- 4.2.10 Timestamps
- 4.2.11 Medium, mode, and function of user inputs:
emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:function, emma:verbal attributes
- 4.2.12 Support for composite multimodality:
emma:hook attribute
- 4.2.13 Cost:
emma:cost attribute
- 4.2.14 Endpoint properties:
emma:endpoint-role, emma:endpoint-address, emma:port-type, emma:port-num, emma:message-id, emma:service-name, emma:endpoint-pair-ref attributes
- 4.2.15 Reference to
emma:grammar element: emma:grammar-ref attribute
- 4.2.16 Reference to
emma:model element: emma:model-ref attribute
- 4.3 Scope of EMMA annotations
- Appendices
1. Introduction
This document presents an XML specification for EMMA, an
Extensible MultiModal Annotation markup language, responding to the
requirements documented in [W3C Requirements for EMMA].
This markup language is intended for use by systems that provide
semantic interpretations for a variety of inputs, including but not
necessarily limited to, speech, natural language text, GUI and ink
input.
It is expected that this markup will be used primarily as a
standard data interchange format between the components of a
multimodal system; in particular, it will normally be automatically
generated by interpretation components to represent the semantics
of users' inputs, not directly authored by developers.
The language is focused on annotating the interpretation
information of single and composed inputs, as opposed to (possibly
identical) information that might have been collected over the
course of a dialog.
The language provides a set of elements and attributes that are
focused on accurately representing annotations on the input
interpretations.
An EMMA document can be considered to hold three types of
data:
-
instance data
Application-specific markup corresponding to input information
which is meaningful to the consumer of an EMMA document. Instances
are application-specific and built by input processors at runtime.
Given that utterances may be ambiguous with respect to input
values, an EMMA document may hold more than one instance.
-
data model
Constraints on structure and content of an instance. The data
model is typically pre-established by an application, and may be
implicit, that is, unspecified.
-
metadata
Annotations associated with the data contained in the instance.
Annotation values are added by input processors at runtime.
Given the assumptions above about the nature of data represented
in an EMMA document, the following general principles apply to the
design of EMMA:
- The main prescriptive content of the EMMA specification will
consist of metadata: EMMA will provide a means to express the
metadata annotations which require standardization. (Notice,
however, that such annotations may express the relationship among
all the types of data within an EMMA document.)
- The instance and its data model are assumed to be specified in
XML, but EMMA will remain agnostic to the XML format used to
express these. (The instance XML is assumed to be sufficiently
structured to enable the association of annotative data.)
-
The extensibility of EMMA lies in the ability for additional
kinds of metadata to be included in application specific
vocabularies. EMMA itself can be extended with application
and vendor specific annotations contained within the
emma:info element.
The annotations of EMMA should be considered 'normative' in the
sense that if an EMMA component produces annotations as described
in Section 3, these annotations must be represented using the EMMA
syntax. The Multimodal Interaction Working Group may address in
later drafts the issues of modularization and profiling, that is:
which sets of annotations are to be supported by which classes of
EMMA component.
1.1 Uses of EMMA
The general purpose of EMMA is to represent information
automatically extracted from a user's input by an interpretation
component, where input is to be taken in the general sense of a
meaningful user input in any modality supported by the platform.
The reader should refer to the sample architecture in [W3C Multimodal Interaction
Framework], which shows EMMA conveying content between user
input modality components and an interaction manager.
Components that generate EMMA markup:
- Speech recognizers
- Handwriting recognizers
- Natural language understanding engines
- Other input media interpreters (e.g. DTMF, pointing,
keyboard)
- Multimodal integration component
Components that use EMMA include:
- Interaction manager
- Multimodal integration component
Although not a primary goal of EMMA, a platform may also choose
to use this general format as the basis of a general semantic
result that is carried along and filled out during each stage of
processing. In addition, future systems may also potentially make
use of this markup to convey abstract semantic content to be
rendered into natural language by a natural language generation
component.
1.2 Terminology
- anchor-point
- When referencing an input interval with
emma:time-ref-uri,
emma:time-ref-anchor allows you to specify whether the
referenced anchor is the start or end of the interval.
- annotation
- Information about the interpreted input, for example,
timestamps, confidence scores, links to raw input, etc.
- composite input
- An input formed from several pieces, often in different modes,
for example, a combination of speech and pen gesture, such
as saying "zoom in here" and circling a region on a map.
- confidence
- A numerical score describing the degree of certainty in
a particular interpretation of user input.
- data model
- For EMMA, a data model defines a set of constraints on
possible interpretations of user input.
- derivation
- Interpretations of user input are said to be derived
from that input, and higher levels interpretations may be
derived from lower level ones. EMMA allows you to reference
the user input or interpretation a given interpretation was
derived from, see semantic interpretation.
- dialogue
- For EMMA, dialogue can be considered as a sequence of
interactions between the users and the application.
- end point
- In EMMA, this refers to a network location which is the
source or receipient of an EMMA document. It should be noted
that the usage of the term "endpoint" in this context is
different from the way that the term is used in speech
processing, where it refers to the end of a speech input.
- gestures
- In multimodal applications gestures are communicative acts
made by the user or application. An example is circling an area
on a map to indicate a region of interest. Users may be able to
gesture with a pen, keystrokes, hand movements or sound. Gestures
often form part of composite input. Application gestures
are typically animations and/or sound effects.
- grammar
- A set of rules that describe a sequence of tokens expected
in a given input. These can be used by speech and handwriting
recognizers to increase recognition accuracy.
- handwriting recognition
- The process of converting pen strokes into text.
- ink recognition
- This includes the recognition of handwriting and pen gestures.
- input cost
- In EMMA, this refers to a numerical measure indicating the
weight or processing cost associated with a user's input or part
of their input.
- input device
- The device proving a particular input, for example, a microphone,
a pen, a mouse, a camera, or a keyboard.
- input function
- In EMMA, this refers to use a particular input is serving, for
example, as part of a recording or transcription, as part of a
dialogue, or as a means to verify the user's identity.
- input medium
- Whether the input is acoustic, visual, or tactile, for instance,
a spoken utterance is an example of an aural input, a hand gesture
as seen by a camera is an example of a visual input, pointing with
a mouse or pen is an example of a tactile input.
- input mode
- This distinguishes a particular means of providing an input
within a general input medium, for example, speech, DTMF, ink,
key strokes, video, photograph, etc.
- input source
- This is the device that provided the input, for example a
particular microphone or camera. EMMA allows you to identify these
with a URI.
- input tokens
- In EMMA, this refers to a sequence of characters, words or
other discrete units of input.
- instance data
- A representation in XML of an interpretation of user input.
- interaction manager
- A processor that determines how an application interacts
with a user. This can be at multiple levels of abstraction, for
example, at a detailed level, determining what prompts to present
to the user and what actions to take in response to user input,
versus a higher level treatment in terms of goals and tasks for
achieving those goals. Interaction managers are typically event
driven.
- interpretation
- In EMMA, an interpretation of user input refers to information
derived from the user input that is meaningful to the application.
- keystroke input
- Input provided by the user pressing on a sequence of keys
(buttons), such as a computer keyboard or keypad.
- lattice
- A set of nodes interconnected with directed arcs such
that by following an arc, you can never find yourself back
at a node you have already visited (i.e. a directed acyclic
graph). Lattices provide a flexible means to represent the
results of speech and handwriting recognition, in terms of
arcs representing words or character sequences. Different
arcs from the same node represent different local hypotheses
as to what the user said or wrote.
- metadata
- Information describing another set of data, for instance,
a library catalog card with information on the author,
title and location of a book. EMMA is designed to support
input processors in providing metadata for interpretations
of user input.
- multimodal integration
- The process of combining inputs from different modes
to create an interpretation of composite input.
This is also sometimes refered to as multimodal
fusion.
- multimodal interaction
- The means for a user to interact with an application
using more than one mode on interaction, for instance,
offering the user the choice of speaking or typing, or
in some cases, allowing the user to provide a composite
input involving multiple modes.
- natural language
understanding
- The process of interpreting text in terms that are
useful for an application.
- N-best list
- An N-best list is a list of the most likely hypotheses for
what the user actually said or wrote, where N stands for an
integral number such as 5 for the 5 most likely hypotheses.
- raw signal
- An uninterpreted input, such as an audio waveform captured
from a microphone.
- semantic interpretation
- A normalized representation of the meaning of a user input,
for instance, mapping the speech for "San Francisco"into the airport code "SFO".
- semantic processor
- In EMMA, this refers to systems that can derive interpretations
of user input, for instance, mapping the speech for "San Francisco"into the airport code "SFO".
- signal interpretation
- The process of mapping a discrete or continuous signal into
a symbolic representation that can be used by an application,
for instance, transforming the audio waveform corresponding to
someone saying "2005" into the number 2005.
- speech recognition
- The process of determining the textual transcription of a
piece of speech.
- speech synthesis
- The process of rendering a piece of text into the corresponding
speech, i.e. synthesising speech from text.
- text to speech
- The process of rendering a piece of text into the corresponding
speech.
- time stamp
- The time that a particular input or part of an input began or
ended.
- URI: Uniform Resource Identifier
- A URI is a unifying syntax for the expression of names and
addresses of objects on the network as used in the World Wide Web.
A URI is defined as any legal
anyURI
primitive as defined in XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes Second Edition Section 3.2.17 [SCHEMA2]. In this specification URIs are
provided as attributes to elements, for example in the
emma:time-ref-uri
attribute.
- user input
- An input provided by a user as opposed to something generated
automatically.
2. Structure of EMMA documents
2.1 Instance data, data model and annotations
As noted above, the main components of an interpreted user input
in EMMA are the instance data, an optional data model, and the
metadata annotations that may be applied to that input. The
realization of these components in EMMA is as follows:
- instance data is contained within an EMMA
interpretation
- the data model is optionally specified as an annotation
of that instance
- EMMA annotations may be applied at different levels of an EMMA
document.
An EMMA interpretation is the primary unit for holding
user input as interpreted by an EMMA processor. As will be seen
below, multiple interpretations of a single input are possible.
EMMA provides a simple structural syntax for the organization of
interpretations and instances, and an annotative syntax to apply
the annotation to the input data at different levels.
An outline of the structural syntax and annotations found in
EMMA documents is as follows. A fuller definition may be found in
the description of individual elements and attributes in section 3 and section 4.
- EMMA Structural Elements (Section 3)
- Root element: The root node of an EMMA document, the
emma:emma element,
holds EMMA version and namespace information, and
provides a container for one or more of the following
interpretation and container elements (Section 3.1)
- Interpretation element:
The
emma:interpretation element contains a given interpretation of
the input and holds application specific markup (Section 3.2)
- Container elements:
emma:one-of is a container
for one or more interpretation elements or container elements and
denotes that these are mutually exclusive interpretations (Section 3.3.1)emma:group is a general
container for one or more interpretation elements or container
elements. It can be associated with arbitrary grouping criteria (Section 3.3.2).emma:sequence is a
container for one or more interpretation elements or container
elements and denotes that these are sequential in time (Section 3.3.3).
- Lattice element: The
emma:lattice
element is used to contain a series of emma:arc and emma:node
elements that define a lattice of words, gestures, meanings or other symbols.
The emma:lattice element appears
within the emma:interpretation element (Section 3.4)
- Literal element: The
emma:literal
element is used as a wrapper when the application semantics is a string literal.
(Section 3.5)
- EMMA annotations (Section 4)
- EMMA annotation elements: These are EMMA annotations
such as
emma:derived-from, emma:endpoint-info, and
emma:info which are represented as elements so that they can occur
more than once within an element and can contain internal structure.
(Section 4.1)
- EMMA annotation attributes: These are EMMA
annotations such as
emma:start, emma:end ,
emma:confidence, and emma:tokens which are represented as attributes.
They can appear on emma:interpretation elements, some can appear on
container elements, lattice elements, and elements in the application-specific markup.
(Section 4.2)
From the defined root node emma:emma the
structure of an EMMA document consists of a tree of EMMA container
elements (emma:one-of,emma:sequence,
emma:group) terminating in a number of interpretation
elements (emma:interpretation). The
emma:interpretation elements serve as wrappers for
either application namespace markup describing the interpretation
of the users input or an emma:lattice element or emma:literal element . A single
emma:interpretation may also appear directly under
the root node.
To illustrate this here is an example EMMA document
for input to a flight reservation application. In this example
there are two speech recognition results and
associated semantic representations of the input. The system
is uncertain whether the user meant "flights from Boston to Denver"or "flights from Austin to Denver". The annotations to be captured
are timestamps and confidence scores for the two inputs.
Example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="r1" emma:start="1087995961542" emma:end="1087995963542">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:confidence="0.75"
emma:tokens="flights from boston to denver">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:confidence="0.68"
emma:tokens="flights from austin to denver">
<origin>Austin</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
Attributes on the root emma:emma element indicate the
version and namespace. The emma:emma element
contains an emma:one-of element which contains
a disjunctive list of possible interpretations of the input. The actual
semantic representation of each interpretation is within the application
namespace. In the example here the application specific semantics involves
elements origin and destination indicating the
origin and destination cities for looking up a flight. The timestamp is the
same for both interpretations and it is annotated using values in
milliseconds in the emma:start
and emma:end attributes on the emma:one-of.
The confidence scores and tokens associated with each of the inputs are annotated
using the EMMA annotation attributes emma:confidence
and emma:tokens
on each of the emma:interpretation elements.
2.2 Data model
An EMMA data model expresses the constraints on the structure
and content of instance data, for the purposes of validation. As
such, the data model may be considered as a particular kind of
annotation (although, unlike other EMMA annotations, it is not a
feature pertaining a specific user input at a specific moment in
time, it is rather a static and, by its very definition,
application-specific structure). Its specification in EMMA is
optional.
Since Web applications today use different formats to specify
data models, e.g. XML Schema, XForms, Relax-NG, etc., EMMA itself
is agnostic to the format of data model used.
Data model definition and reference is defined in Section 4.1.1.
2.3 EMMA namespace prefixes
An EMMA attribute is prefixed with the EMMA namespace identifier if the attribute
can also be used as an in-line annotation on elements in the application's namespace.
Most of the EMMA annotation attributes in Section 4.2 are in this category. An EMMA attribute
is not prefixed if the attribute only appears on an EMMA element. This rule ensures
consistent usage of the attributes across all examples.
2.4 Conformance
2.4.1 Conforming EMMA Documents
A document is a Conforming EMMA Document if it meets both the
following conditions:
- It is a well-formed XML document [XML] conforming
to Namespaces in XML [XMLNS].
- It adheres to the specification described in this document (EMMA
Specification) including the constraints expressed in the Schema (see Appendix A) and having an XML Prolog and root element as
specified in Section 3.1.
The EMMA specification and these conformance criteria provide no
designated size limits on any aspect of EMMA documents. There are
no maximum values on the number of elements, the amount of character
data, or the number of characters in attribute values.
2.4.2 Using EMMA with other Namespaces
The EMMA namespace is intended to be used with other XML namespaces
as per the Namespaces in XML Recommendation [XMLNS]. Future work by
W3C is expected to address ways to specify conformance for documents
involving multiple namespaces.
2.4.3 Conforming EMMA Processors
A EMMA processor is a program that can process and/or
generate Conforming EMMA documents.
In a Conforming EMMA Processor, the XML parser must be able to parse
and process all XML constructs defined by XML 1.0 [XML] and
Namespaces in XML [XMLNS]. It is not required that a
Conforming EMMA Processor uses a validating XML parser.
A Conforming EMMA Processor must correctly understand and apply the
semantics of each markup element or attribute as described by this document.
There is, however, no conformance requirement with respect to
performance characteristics of the EMMA Processor. For instance,
no statement is required regarding the accuracy, speed or other
characteristics of output produced by the processor. No statement
is made regarding the size of input that a EMMA Processor must support.
3. EMMA structural elements
This section defines elements in the EMMA namespace which
provide the structural syntax of EMMA documents.
3.1 Root element: emma:emma
| Annotation |
emma:emma |
| Definition |
The root element of an EMMA document. |
| Children |
The emma:emma element must immediately contain
a single emma:interpretation element or EMMA container element:
emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence.
It may also contain an optional single emma:derivation element
and an optional single emma:info annotation element.
It may also contain multiple optional emma:grammar annotation elements,
emma:model annotation elements, and emma:endpoint-info annotation elements. |
| Attributes |
- Required:
version: the version of EMMA used for the
interpretation(s). Interpretations expressed using this
specification must use 1.0 for the value.- Namespace declaration for EMMA, see below.
- Optional:
- any other namespace declarations for application
specific namespaces.
|
| Applies to |
None |
The root element of an EMMA document is named emma:emma. It
holds a single emma:interpretation or EMMA container element (emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, emma:group). It can also optionally contain a
single emma:derivation element containing earlier stages of the
processing of the input (See Section 4.1.2). It can also contain
an optional single annotation element: emma:info
and multiple optional emma:grammar, emma:model,
and emma:endpoint-info elements.
It can hold attributes for information pertaining to EMMA itself, along with
any namespaces which are declared for the entire document, and any
other EMMA annotative data. The emma:emma element and other elements and
attributes defined in this specification belong to the XML
namespace identified by the URI "http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma".
In the examples, the EMMA namespace is generally declared using the
attribute xmlns:emma on the root emma:emma element. EMMA processors must
support the full range of ways of declaring XML namespaces as
defined by the W3C Recommendation "Namespaces in XML 1.1" [XMLNS]. Application markup can be declared in an
explicit application namespace, or an undefined namespace
(equivalent to setting xmlns="").
For example:
<emma:emma version="1.0" xmlns:emma="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma">
....
</emma:emma>
or
<emma version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma">
....
</emma>
3.2 Interpretation element: emma:interpretation
| Annotation |
emma:interpretation |
| Definition |
The emma:interpretation element
acts as a wrapper for application instance data or lattices.
|
| Children |
The emma:interpretation element must immediately contain either application
instance data, or a single emma:lattice element, or a single emma:literal element,
or in the case of uninterpreted input or no input emma:interpretation can be empty.
It can also contain an optional one or more of the emma:derived-from
element and one of the optional annotation elements emma:info.
|
| Attributes |
- Required: Attribute
id of type xsd:ID that uniquely identifies the interpretation within the EMMA document.
- Optional: The annotation attributes:
emma:tokens, emma:process, emma:no-input, emma:uninterpreted, emma:lang, emma:signal, emma:media-type, emma:confidence, emma:source, emma:start, emma:end, emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point, emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration, emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:function, emma:verbal, emma:cost, emma:grammar-ref, emma:endpoint-info-ref, emma:model-ref.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:interpretation element can only appear as a child of emma:emma, emma:group, emma:one-of, emma:sequence, or emma:derivation. |
The emma:interpretation element holds a single
interpretation represented in application specific markup, or a single emma:lattice
element, or a single emma:literal element.
The emma:interpretation element can also be empty
but it must be annotated with either emma:no-input="true" or
emma:uninterpreted="true".
If emma:interpretation is marked with emma:no-input="true" then
it must be empty.
Attributes:
- id a required
xsd:ID value that uniquely identifies the
interpretation within the EMMA document.
<emma:emma version="1.0" xmlns:emma="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma">
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="r1">
...
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
3.3 Container elements
3.3.1 emma:one-of element
| Annotation |
emma:one-of |
| Definition |
A container element indicating a disjunction among a collection of
mutually exclusive interpretations of the input. |
| Children |
The emma:one-of element must immediately contain
a collection of one or more emma:interpretation elements or container elements:
emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence .
It can also contain an optional one or more of the emma:derived-from
element and one of the optional annotation elements emma:info.
|
| Attributes |
- Required: Attribute
id of type xsd:ID
- Optional: The annotation attributes:
emma:tokens, emma:process, emma:lang, emma:signal, emma:media-type, emma:confidence, emma:source, emma:start, emma:end, emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point, emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration, emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:function, emma:verbal, emma:cost, emma:grammar-ref, emma:endpoint-info-ref, emma:model-ref.
|
|---|
| Applies to |
The emma:one-of element can only appear as a child of emma:emma, emma:one-of, emma:group,
emma:sequence, or emma:derivation. |
The emma:one-of element acts a
container for a collection of one or more interpretation (emma:interpretation) or container
elements (emma:one-of, emma:group,
emma:sequence), and denotes that these are mutually exclusive
interpretations.
An N-best list of choices in EMMA, such
as a series of different recognition results in speech recognition,
should be represented as a set of emma:interpretation
elements contained within an emma:one-of element.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="r1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<origin>Austin</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
The interpretations must be sorted best-first by some measure of
quality. The quality measure is emma:confidence if
present, otherwise, the quality metric is platform-specific.
The emma:one-of element can
appear within another emma:one-of
element, allowing for easy combination of N-best lists from
different devices or recognizers processing the same signal. This
also allows for annotations which apply to a subset of an N-best
list to be specified once on a emma:one-of element embedded within another
emma:one-of element.
3.3.2 emma:group element
| Annotation |
emma:group |
| Definition |
A container element indicating that a number of interpretations
of distinct user inputs are grouped according to some criteria. |
| Children |
The emma:group element must immediately contain
a collection of one or more emma:interpretation elements or container elements:
emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence .
It may also contain an optional emma:group-info element.
It can also contain an optional one or more of the emma:derived-from
element and one of the optional annotation elements emma:info.
|
| Attributes |
- Required: Attribute
id of type xsd:ID
- Optional: The annotation attributes:
emma:tokens, emma:process, emma:lang, emma:signal, emma:media-type, emma:confidence, emma:source, emma:start, emma:end, emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point, emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration, emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:function, emma:verbal, emma:cost, emma:grammar-ref, emma:endpoint-info-ref, emma:model-ref.
|
|---|
| Applies to |
The emma:group element can only appear as a child of emma:emma, emma:one-of, emma:group,
emma:sequence, or emma:derivation. |
The
emma:group element is used to indicate that the contained
interpretations are from distinct user inputs that are related in some
manner. emma:group should not be used for containing
the multiple stages of processing of a single user input. Those should be
contained in the emma:derivation element instead.
For groups of inputs in temporal order the more specialized container emma:sequence
should be used. The following example shows three interpretations derived from the speech input "Move
this ambulance here" and the tactile input related to two
consecutive points on a map.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:group id="grp"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995964542">
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<action>move</action>
<object>ambulance</object>
<destination>here</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<x>0.253</x>
<y>0.124</y>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int3">
<x>0.866</x>
<y>0.724</y>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:group>
</emma:emma>
The emma:one-of and emma:group containers can be
nested arbitrarily.
3.3.2.1 Indirect grouping criteria: emma:group-info element
| Annotation |
emma:group-info |
| Definition |
The emma:group-info element contains or references
criteria used in establishing the grouping of interpretations in an emma:group
element. |
| Children |
The emma:group-info element either immediately contains inline instance
data specifying grouping criteria or has the attribute ref referencing
the criteria.
|
| Attributes |
- Optional:
ref of type xsd:anyURI
referencing the grouping criteria, alternatively the criteria can
be provided inline as the content of the emma:group-info element
. |
|---|
| Applies to |
The emma:group-info element can only appear as a child of emma:group. |
Sometimes it may be convenient to indirectly associate a given
group with information, such as grouping criteria. The
emma:group-info element can be used to
make explicit the criteria by which members of a group are
associated.
In the following example, a group of two points is associated with
a description of grouping criteria based upon a sliding temporal
window of two seconds duration.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example"
xmlns:ex="http://www.example.com/ns/group">
<emma:group id="grp">
<emma:group-info>
<ex:mode>temporal</ex:mode>
<ex:duration>2s</ex:duration>
</emma:group-info>
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<x>0.253</x>
<y>0.124</y>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<x>0.866</x>
<y>0.724</y>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:group>
</emma:emma>
You can also use emma:group-info to refer to a named
grouping criterion using external reference, for instance:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example"
xmlns:ex="http://www.example.com/ns/group">
<emma:group id="grp">
<emma:group-info ref="http://www.example.com/criterion42"/>
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<x>0.253</x>
<y>0.124</y>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<x>0.866</x>
<y>0.724</y>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:group>
</emma:emma>
3.3.3 emma:sequence element
| Annotation |
emma:sequence |
| Definition |
A container element indicating that a number of interpretations
of distinct user inputs are in temporal sequence. |
| Children |
The emma:sequence element must immediately contain
a collection of one or more emma:interpretation elements or container elements:
emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence .
It can also contain an optional one or more of the emma:derived-from
element and one of the optional annotation element emma:info.
|
| Attributes |
- Required: Attribute
id of type xsd:ID
- Optional: The annotation attributes:
emma:tokens, emma:process, emma:lang, emma:signal, emma:media-type, emma:confidence, emma:source, emma:start, emma:end, emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point, emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration, emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:function, emma:verbal, emma:cost, emma:grammar-ref, emma:endpoint-info-ref, emma:model-ref.
|
|---|
| Applies to |
The emma:sequence element can only appear as a child of emma:emma, emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence, or emma:derivation. |
The
emma:sequence element is used to indicate that the contained
interpretations are sequential in time, as in the following
example, which indicates that two points made with a pen are
in temporal order.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:sequence id="seq1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink">
<x>0.253</x>
<y>0.124</y>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink">
<x>0.866</x>
<y>0.724</y>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:sequence>
</emma:emma>
The emma:sequence container can be combined with
emma:one-of and emma:group in arbitrary nesting
structures. The order of children in the content of the emma:sequence
element corresponds to a sequence of interpretations. This
ordering does not imply any particular definition of sequentiality.
EMMA processors may therefore use the emma:sequence element to hold
interpretations which are either strictly sequential in nature
(e.g. the end-time of an interpretation precedes the start-time of
its follower), or which overlap in some manner (e.g. the start-time
of a follower interpretation precedes the end-time of its
precedent). It is possible to use timestamps to provide fine grained
annotation for the sequence of interpretations that are sequential
in time.
In the following more complex example, a sequence of two pen gestures in
emma:sequence and a speech input in emma:interpretation
are contained in an emma:group.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:group id="grp">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech">
<action>move</action>
<object>this-battleship</object>
<destination>here</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:sequence id="seq1">
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink">
<x>0.253</x>
<y>0.124</y>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int3" emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink">
<x>0.866</x>
<y>0.724</y>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:sequence>
</emma:group>
</emma:emma>
3.4 Lattice element
In addition to providing the ability to represent N-best lists
of interpretations using emma:one-of, EMMA also
provides the capability to represent lattices of words or other
symbols using the emma:lattice element. Lattices
provide a compact representation of large lists of possible
recognition results or interpretations for speech, pen, or
multimodal inputs.
In addition to providing a representation for lattice output
from speech recognition, another important use case for lattices is
for representation of the results of gesture and handwriting
recognition from a pen modality component. Lattices can also be
uses to compactly represent multiple possible meaning
representations. Another use case for the lattice representation is
that it enables the association of confidence scores and other
annotations with individual words within a speech recognition
result string.
Lattices can be compactly described by a list of transitions
between nodes. For each transition the start and end nodes need to
be defined, along with the label for the transition. Initial and
final nodes also need to be indicated. The following figure
provides a graphical representation of a speech recognition lattice
which compactly represents eight different sequences of words.
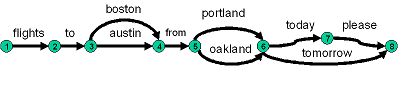
which expands to:
a. flights to boston from portland today please
b. flights to austin from portland today please
c. flights to boston from oakland today please
d. flights to austin from oakland today please
e. flights to boston from portland tomorrow
f. flights to austin from portland tomorrow
g. flights to boston from oakland tomorrow
h. flights to austin from oakland tomorrow
3.4.1 Lattice markup: emma:lattice, emma:arc, emma:node elements
| Annotation |
emma:lattice |
| Definition |
An element which encodes a lattice
representation of user input.
|
| Children |
The emma:lattice element immediately contains one or more emma:arc elements and zero or more emma:node elements.
|
| Attributes |
- Required:
initial has an integer value
indicating the number of the initial node of the lattice.final contains a space delimited sequence of integers
indicating the numbers of the final nodes in the lattice. .
- Optional:
emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point
.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:lattice element can only appear as a child of the emma:interpretation element. |
| Annotation |
emma:arc |
| Definition |
An element which encodes a transition between
two nodes in a lattice. The label associated with the arc in the lattice is
represented in the content of emma:arc.
|
| Children |
The emma:arc
element can immediately contain either character data or a single application namespace element or
be empty, in the case of epsilon transitions.
It can also contain an optional emma:info element containing application
or vendor specific annotations.
|
| Attributes |
- Required:
from has an integer value
indicating the number of the starting node for the arc.to has an integer value indicating
the number of the ending node for the arc .
- Optional:
emma:start, emma:end, emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration, emma:confidence, emma:cost, emma:lang, emma:medium, emma:mode, emma:source
.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:arc element can only appear as a child of the emma:lattice element. |
| Annotation |
emma:node |
| Definition |
An element which represents a node in the
lattice. The emma:node elements are not
required to describe a lattice but can be added to provide a
location for annotations on nodes in a lattice. There can only be
one emma:node specification for each numbered node
in the lattice. |
| Children |
An optional emma:info element for application or vendor specific
annotations on the node.
|
| Attributes |
- Required:
node-number has an integer value
indicating the number of node in the lattice.
- Optional:
emma:start, emma:end, emma:offset-to-start,
emma:confidence, emma:cost
.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:node element can only appear as a child of the emma:lattice element. |
In EMMA, a lattice is represented using an element
emma:lattice, which has attributes
initial and final for indicating the
initial and final nodes of the lattice. For the lattice above, this
will be: <emma:lattice initial="1"final="8"/>. The nodes are numbered with integers. If
there is more than one distinct final node in the lattice the nodes
should be represented as a space separated list in the value of the
final attribute e.g. <emma:lattice
initial="1" final="9 10 23"/>. There can only be
one initial node in an EMMA lattice. Each transition in the lattice is
represented as an element emma:arc with attributes
from and to which indicate the nodes where
the transition starts and ends. The arc's label is represented as
the content of the emma:arc element, and can be any
well-formed character or XML content. In the example here the
contents are words. Empty (epsilon) transitions in a lattice should
be represented in the emma:lattice representation as
emma:arc elements with no content, e.g
<emma:arc from="1" to="8"/>.
The example speech lattice above would be represented in EMMA
markup as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<emma:lattice initial="1" final="8">
<emma:arc from="1" to="2">flights</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="2" to="3">to</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="3" to="4">boston</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="3" to="4">austin</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="4" to="5">from</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="5" to="6">portland</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="5" to="6">oakland</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="6" to="7">today</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="7" to="8">please</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="6" to="8">tomorrow</emma:arc>
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
Alternatively, if we wish to represent the same information as an
N-best list using emma:one-of, we would have the more
verbose representation:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<text>flights to boston from portland today please</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretationid="interp2">
<text>flights to boston from portland tomorrow</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp3">
<text>flights to austin from portland today please</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp4">
<text>flights to austin from portland tomorrow</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp5">
<text>flights to boston from oakland today please</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp6">
<text>flights to boston from oakland tomorrow</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp7">
<text>flights to austin from oakland today please</text>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp8">
<text>flights to austin from oakland tomorrow</text>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
The lattice representation avoids the need to enumerate all of
the possible word sequences. Also, as detailed below, the
emma:lattice representation enables placement of
annotations on individual words in the input.
For use cases involving the representation of gesture/ink
lattices and use cases involving lattices of semantic
interpretations, EMMA allows for application namespace elements to
appear within emma:arc.
For example a sequence of two gestures, each of which is
recognized as either a line or an circle could be represented as
follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<emma:lattice initial="1" final="3">
<emma:arc from="1" to="2">
<circle radius="100"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="2" to="3">
<line length="628"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="1" to="2">
<circle radius="200"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="2" to="3">
<line length="1256"/>
</emma:arc>
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
As an example of a lattice of semantic interpretations, in a
travel application where the source is either "Boston" or "Austin"and the destination is either "Newark" or "New York", the
possibilities could be represented in a lattice as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<emma:lattice initial="1" final="3">
<emma:arc from="1" to="2">
<source city="boston"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="2" to="3">
<destination city="newark"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="1" to="2">
<source city="austin"/>
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc from="2" to="3">
<destination city="new york"/>
</emma:arc>
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The emma:arc element can contain either an application
namespace element or character data. It cannot contain combinations
of application namespace elements and character data. However, an
emma:info element can appear within an emma:arc
element
alongside character data, in order to allow for the association of
vendor or application specific annotations on a single word or symbol in a
lattice.
So, in summary, there are four groupings of content that can
appear within emma:arc:
- Character Data e.g. a recognized word in a speech lattice.
- Character Data and a single
emma:info element
providing vendor or application specific annotations that apply to
the character data.
- An application namespace element e.g. the gesture and meaning
lattice examples above.
- An application namespace element and a single
emma:info element providing vendor or application
specific annotations that apply to the character data.
3.4.2 Annotations on lattices
The encoding of lattice arcs as XML elements
(emma:arc) enables arcs to be annotated with
metadata such as timestamps, costs, or confidence scores:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<emma:lattice initial="1" final="8">
<emma:arc
from="1"
to="2"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995962042"
emma:cost="30">
flights
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="2"
to="3"
emma:start="1087995962042"
emma:end="1087995962542"
emma:cost="20">
to
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="3"
to="4"
emma:start="1087995962542"
emma:end="1087995963042"
emma:cost="50">
boston
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="3"
to="4"
emma:start="1087995963042"
emma:end="1087995963742"
emma:cost="60">
austin
</emma:arc>
...
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The following EMMA attributes may optionally be placed on
emma:arc elements: absolute timestamps
(emma:start, emma:end), relative timestamps (
emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration),
emma:confidence, emma:cost, the human language of the
input (emma:lang), emma:medium, emma:mode, and
emma:source. The use case for emma:medium,
emma:mode, and emma:source is for lattices which
contains content from different input modes. The
emma:arc element can also contain an optional
emma:info element for specification of vendor and
application specific annotations on the arc.
Costs are typically application and device dependent. There are
a variety of ways that individual arc costs can be combined to
produce costs for specific paths through the lattice. This
specification does not standardize the way for these costs to be
combined; it is up to the applications and devices to determine how
such derived costs would be computed and used.
For some lattice formats, it is also desirable to annotate the
nodes in the lattice themselves with information such as costs. For
example in speech recognition, costs may be placed on nodes as a
result of word penalities or redistribution of costs. For this
purpose EMMA also provides an emma:node element
which can host annotations such as emma:cost.
The emma:node element must have an attribute
node-number which indicates the number of the node.
There can only be one emma:node specification for a
given numbered node in the lattice. In our example, if there was a
cost of 100 on the final state this could be represented as
follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1">
<emma:lattice initial="1" final="8">
<emma:arc
from="1"
to="2"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995962042"
emma:cost="30">
flights
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="2"
to="3"
emma:start="1087995962042"
emma:end="1087995962542"
emma:cost="20">
to
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="3"
to="4"
emma:start="1087995962542"
emma:end="1087995963042"
emma:cost="50">
boston
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="3"
to="4"
emma:start="1087995963042"
emma:end="1087995963742"
emma:cost="60">
austin
</emma:arc>
...
<emma:node node-number="8" emma:cost="100"/>
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
3.4.3 Relative timestamps on lattices
The relative timestamp mechanism in EMMA can be used to provide
temporal information about arcs in a lattice in relative terms
using offsets in milliseconds. In order to do this the absolute
time should be specified on emma:interpretation.
Since emma:time-ref-uri and emma:time-ref-anchor-point
apply to emma:lattice and can be used there to set
the anchor point for offset to the start of the absolute time
specified on emma:interpretation. The offset in
milliseconds to the beginning of each arc can then be indicated on
each emma:arc in the emma:offset-to-start
attribute.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1"
emma:start="1087995961542" emma:end="1087995963042">
<emma:lattice emma:time-ref-uri="#interp1"
emma:time-ref-anchor-point="start"
initial="1" final="4">
<emma:arc
from="1"
to="2"
emma:offset-to-start="0">
flights
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="2"
to="3"
emma:offset-to-start="500">
to
</emma:arc>
<emma:arc
from="3"
to="4"
emma:offset-to-start="1000">
boston
</emma:arc>
</emma:lattice>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
Note that the offset for the first emma:arc will
always be zero since the EMMA attribute emma:offset-to-start
indicates the number of milliseconds from the anchor point to the
start of the piece of input associated with the
emma:arc, in this case the word "flights".
3.5 Literal semantics: emma:literal element
| Annotation |
emma:literal |
| Definition |
An element that contains string literal output.
|
| Children |
String literal
|
| Attributes |
None.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:literal is a child of emma:interpretation. |
Certain EMMA processing components may produce semantic results in the form of
string literals without any surrounding application namespace markup. These should be
placed with the EMMA element emma:literal within emma:interpretation.
For example, if a semantic interpreter simply returned "boston" this could be represented in EMMA
as:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation>
<emma:literal>boston</emma:literal>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4. EMMA annotations
This section defines annotations in the EMMA namespace including
both attributes and elements. The values are specified in terms of
the data types defined by XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes [XSD].
4.1 EMMA annotation elements
4.1.1 Data model: emma:model element
| Annotation |
emma:model |
| Definition |
The emma:model either references or provides
inline the data model for the instance data.
|
| Children |
If a ref attribute is not specified then this element
contains the data model inline. |
| Attributes |
- Required:
- Optional:
ref of type xsd:anyURI that references
the data model. Note that either an ref attribute or in-line data model (but not
both) must be specified.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:model element can only be a child of emma:emma. |
The data model that may be used to express constraints on the
structure and content of instance data is specified as one of the
annotations of the instance. Specifying the data model is optional,
in which case the data model can be said to be implicit. Typically
the data model is pre-established by the application.
The data model is specified with the emma:model
annotation defined as an element in the EMMA namespace. The attribute
emma:model-ref must be specified on emma:interpretation,
container elements, or application namespace elements in order to refer to
the data model for the contents of that element.
Note that
since multiple emma:model elements can be
specified under the emma:emma it is
possible to refer to multiple data models in
within a single EMMA document. For example, different
alternative interpretations under an emma:one-of
might have different data models. In this case, an emma:model-ref
attribute would appear on each emma:interpretation element
in the N-best list with its value being the id of the
emma:model element for that particular interpretation.
The data model is closely related to the interpretation data,
and is typically specified as the annotation related to the
emma:interpretation or emma:one-of elements.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:model id="model1" ref="http://myserver/models/city.xml"/>
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:model-ref="model1">
<city> London </city>
<country> UK </country>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The emma:model annotation can reference any element or
attribute in the application instance data, as well as any EMMA
container element (emma:one-of, emma:group, or
emma:sequence).
The data model annotation can be used to either reference an
external data model with the "ref" attribute or provide a data
model as in-line content. Either a "ref" attribute or in-line data
model (but not both) must be specified.
4.1.2 Interpretation derivation: emma:derived-from element and emma:derivation element
| Annotation |
emma:derived-from |
| Definition |
An empty element which provides a reference to the interpretation which
the element it appears on was derived from. |
| Children |
None |
| Attributes |
- Required:
resource of type
xsd:anyURI that references the interpretation from which the
current interpretation is derived.
- Optional:
composite of type xsd:boolean that is
"true" if the derivation step combines multiple inputs and "false" if not.
If composite is not specified the value is "false" by default.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:derived-from element can only appear as a child of emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group, or emma:sequence. |
| Annotation |
emma:derivation |
| Definition |
An element which contains interpretation and container elements representing
earlier stages in the processing of the input. |
| Children |
One or more emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:sequence, or emma:group elements. |
| Attributes |
None
|
| Applies to |
The emma:derivation can only be a child of the emma:emma element. |
Instances of interpretations are in general derived from other
instances of interpretation in a process that goes from raw data to
increasingly refined representations of the input. The derivation
annotation is used to link any two interpretations that are related
by representing the source and the outcome of an interpretation
process. For instance, a speech recognition process can return the
following result in the form of raw text:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="raw">
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
A first interpretation process will produce:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="better">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
A second interpretation process, aware of the current date, will
be able to produce a more refined instance, such as:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="best">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>20030315</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The interaction manager may need to have access to the three
levels of interpretation. The emma:derived-from annotation element can be
used to establish a chain of derivation relationships as in the
following example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="raw">
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="better">
<emma:derived-from resource="#raw" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="best">
<emma:derived-from resource="#better" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>20030315</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The emma:derivation element is used as a container for representations of the
earlier stages in the interpretation of the input. The latest stage of processing a direct child of emma:emma.
In order to indicate whether an emma:derived-from
element describes a sequential derivation step or a composite
derivation step, the emma:derived-from element has an attribute
composite which has a boolean value. A composite
emma:derived-from needs to be marked as
composite="true" while a sequential
emma:derived-from element is marked as composite="false".
If this attribute is not specified the value is false by default.
In annotating derivations of the processing of the input, EMMA provides the
flexibility of both course-grained or fine-grained annotation of relations
among interpretations. For example, when relating two N-best lists, within
emma:one-of elements either there can be a single emma:derived-from
element under emma:one-of referring to the ID of the emma:one-of for the earlier processing stage:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="nbest2">
<emma:derived-from resource="#nbest1" composite="false"/>
<emma:interpretation id="int1b">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2b">
<origin>Austin</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
<emma:derivation>
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<result>from boston to denver on march eleven two thousand three</result>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<result>from austin to denver on march eleven two thousand three</result>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:derivation>
</emma:emma>
Or there can be a separate emma:derived-from element on each
emma:interpretation element referring to the specific
emma:interpretation element it was derived from.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="nbest2">
<emma:interpretation id="int1b">
<emma:derived-from resource="#int1" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2b">
<emma:derived-from resource="#int2" composite="false"/>
<origin>Austin</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
<emma:derivation>
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<result>from boston to denver on march eleven two thousand three</result>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2">
<result>from austin to denver on march eleven two thousand three</result>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:derivation>
</emma:emma>
Section 4.3 provides further examples of the
use of emma:derived-from to represent both
sequential derivations like those above and composite derivations
in which inputs from multiple different modalities are combined,
and addresses the issue of the scope of EMMA annotations across
derivations of user input.
4.1.3 Reference to grammar used: emma:grammar element
| Annotation |
emma:grammar |
| Definition |
An element used to provide a reference to the grammar used in processing the input. |
| Children |
None |
| Attributes |
- Required:
href of type xsd:anyURI that references
a grammar used in processing the input.id of type xsd:ID.
|
| Applies to |
The emma:grammar can only appear as a child of the emma:emma element. |
The grammar that was used to derive the EMMA result is specified
with the emma:grammar annotation defined as an element in
the EMMA namespace.
Example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:grammar id="gram1" href="someURI"/>
<emma:grammar id="gram2" href="anotherURI"/>
<emma:one-of id="r1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:grammar-ref="gram1">
<origin>Boston</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:grammar-ref="gram1">
<origin>Austin</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int3" emma:grammar-ref="gram2">
<command>help</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
The emma:grammar annotation is a child of
emma:emma.
4.1.4 Extensibility to application/vendor specific
annotations: emma:info element
| Annotation |
emma:info |
| Definition |
The emma:info element acts as a container for vendor and/or application specific
metadata regarding a user's input. |
| Children |
Elements in the application namespace providing
metadata about the input. |
| Attributes |
|
| Applies to |
The emma:info element can only appear as a child of
the EMMA elements emma:emma,
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, emma:arc, or emma:node. |
In Section 3.2, a series of attributes are
defined for representation of metadata about user inputs in a
standardized form. EMMA also provides an extensibility mechanism
for annotation of user inputs with vendor or application specific
metadata not covered by the standard set of EMMA annotations. The
element emma:info should be used as a container for
these annotations. For example, if an input to a dialog system
needed to be annotated with the number that the call originated
from, their state, some indication of the type of customer, and the
name of the service, these pieces of information could be
represented within emma:info as in the following
example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:info>
<caller_id>
<phone_number>2121234567</phone_number>
<state>NY</state>
</caller_id>
<customer_type>residential</customer_type>
<service_name>acme_travel_service</service_name>
</emma:info>
<emma:one-of id="r1" emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:confidence="0.75">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:confidence="0.68">
<origin>Austin</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03112003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
It is important to have an EMMA container element for
application/vendor specific annotations since EMMA elements provide
a structure for representation of multiple possible interpretations
of the input. As a result it is cumbersome to state
application/vendor specific metadata as part of the application
data within each emma:interpretation. An element is
used rather than an attribute so that internal structure can be
given to the annotations within emma:info.
In addition to emma:emma,
emma:info can also appear as a child of other
structural elements such as emma:interpretation,
emma:info and so on. When emma:info
appears as a child of one of these elements the application/vendor
specific annotations contained within emma:info are
assumed to apply to all of the emma:interpretation
elements within the containing element. The semantics of
conflicting annotations in emma:info, for example
when different values are found within emma:emma and
emma:interpretation, are left to the developer of
the vendor/application specific annotations.
4.1.5 Endpoint reference: emma:endpoint-info element and emma:endpoint element
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint-info |
| Definition |
The emma:endpoint-info element acts as a container for all application specific
annotation regarding the communication environment. |
| Children |
One or more emma:endpoint elements. |
| Attributes |
|
| Applies to |
The emma:endpoint-info elements can only appear as a child of emma:emma. |
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint |
| Definition |
The element acts as a container for application specific endpoint information. |
| Children |
Elements in the application namespace providing metadata about the input. |
| Attributes |
- Required:
- Optional:
emma:endpoint-role, emma:endpoint-address, emma:message-id,
emma:port-num, emma:port-type, emma:endpoint-pair-ref,
emma:service-name, emma:media-type, emma:medium,
emma:mode.
|
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint-info |
In order to conduct multimodal interaction, there is a need in
EMMA to specify the properties of the endpoint that receives the
input which leads to the EMMA annotation. This allows
subsequent components to utilize the endpoint properties as well as
the annotated inputs to conduct meaningful multimodal interaction.
EMMA element emma:endpoint can be used for this
purpose. It can specify the endpoint properties based on a set of
common endpoint property attributes in EMMA, such as
emma:endpoint-address, emma:port-num, emma:port-type, etc. (See
Section 4.2.14).
Moreover, it provides an extensible annotation structure that
allows the inclusion of application and vendor specific endpoint
properties.
It should be noted that the usage of the term "endpoint" in this
context is different from the way that the term is used in speech
processing, where it refers to the end of a speech input. As used
here, "endpoint" refers to a network location which is the source
or receipient of an EMMA document.
In multimodal interaction, multiple devices can be used and each
device can open multiple communication endpoints at the same time.
These endpoints are used to transmit and receive data, such as raw
input, EMMA documents, etc. Moreover, these communication endpoints
can be based on a varity of protocols and data formats, such as
SIP, TCP, SOAP, HTTP, SMTP, MRCP, etc. The EMMA element
emma:endpoint provides a generic
representation of endpoint information which is relevant to
multimodal interaction. It allows the annotation to be
interoperable, and it eliminates the need for EMMA processors to
create their own specialized annotations for existing protocols,
potential protocols or yet undefined private protocols that they
may use.
Moreover, emma:endpoint-info provides a container
to hold all annotations regarding the endpoint information,
including emma:endpoint and other application and
vendor specific annotations that are related to the communication,
allowing the same communication environment to be referenced and
used in multiple interpretations.
It should be noted that EMMA provides two locations (i.e.
emma:info and emma:endpoint-info) for specifying
vendor/application specific annotations. If the annotation is
specifically related to the description of the endpoint, then the
vendor/application specific annotation should be placed within
emma:endpoint-info, otherwise it should be placed within
emma:info.
The following example illustrates the annotation of endpoint
reference properties in EMMA.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example"
xmlns:ex="http://www.example.com/emma/port">
<emma:endpoint-info id="audio-channel-1">
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint1"
emma:endpoint-role="sink"
emma:endpoint-address="135.61.71.103"
emma:port-num="50204"
emma:port-type="rtp"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint2"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel"
emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint2"
emma:endpoint-role="source"
emma:endpoint-address="136.62.72.104"
emma:port-num="50204"
emma:port-type="rtp"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint1"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel"
emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
</emma:endpoint-info>
<emma:interpretation id="int1"
emma:start="1087995961542" emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:endpoint-info-ref="audio-channel-1">
<destination>Chicago</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The ex:app-protocol is provided by the
application or the vendor specification. It specifies that the
application layer protocol used to establish the speech
transmission from the "source" port to the "sink" port is Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP). This is specific to SIP based VoIP
communication, in which the actual media transmission and the call
signaling that controls the communication sessions, are separated
and typically based on different protocols. In the above example,
the Real-time Transmission Protocol (RTP) is used in the media
transmission between the source port and the sink port.
4.2 EMMA annotation attributes
4.2.1 Tokens of input: emma:tokens attribute
| Annotation |
emma:tokens |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string holding a sequence of input
tokens. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, and application instance data. |
The emma:tokens annotation holds a list of input tokens.
In the following description, the term tokens is used in the
computational and syntactic sense of units of input, and not
in the sense of XML tokens.
The value held in emma:tokens is the list of the tokens
of input as produced by the processor which generated the EMMA
document. In the case where a grammar is used to constrain input,
the value will correspond to tokens as defined by the grammar. So
for an EMMA document produced by input to a W3C SRGS grammar
[SRGS], the value of emma:tokens will be
the list of words and/or phrases that are defined as tokens in SRGS
(through white-spaced character data or the token;
element, see SRGS (Section 2.1
Tokens). Items in the emma:tokens list are delimited by
white space and/or quotation marks for phrases containing white
space. For example:
emma:tokens="arriving at 'Liverpool Street'"
where the three tokens of input are arriving, at
and Liverpool Street.
The tokens annotation may be applied not just to the lexical
words and phrases of language but to any level of input processing.
Other examples of tokenization include phonemes, ink strokes,
gestures and any other discrete units of input at any level.
Examples:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="int1"
emma:tokens="From Cambridge to London tomorrow">
<origin emma:tokens="From Cambridge">Cambridge</origin>
<destination emma:tokens="to London">London</destination>
<date emma:tokens="tomorrow">20030315</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.2 Reference to processing: emma:process attribute
| Annotation |
emma:process |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI referencing the process used to
generate the interpretation. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence |
A reference to the information concerning the processing that
was used for generating an interpretation can be made as in the
following example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="raw">
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="better"
emma:process="http://example.com/mysemproc1.xml">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
<emma:derived-from resource="#raw"/>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="best"
emma:process="http://example.com/mysemproc2.xml">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
<emma:derived-from resource="#better"/>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The process description document, referenced by the
emma:process annotation can include information on the
process itself, such as grammar, type of parser, etc. EMMA is not
normative about the format of the process description document.
4.2.3 Lack of input: emma:no-input attribute
| Annotation |
emma:no-input |
| Definition |
Attribute holding xsd:boolean value that is true if there was
no input. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation |
The case of lack of input can be annotated as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:no-input="true" />
</emma:emma>
If the emma:interpretation is annotated with
emma:no-input="true" then the
emma:interpretation must be empty. The
emma:interpretation is empty only if the
emma:interpretation is annotated with either
emma:no-input="true" or
emma:uninterpreted="true".
4.2.4 Uninterpretable input: emma:uninterpreted attribute
| Annotation |
emma:uninterpreted |
| Definition |
Attribute holding xsd:boolean value that is true if the input
could not be interpreted |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation |
Input that cannot be interpreted is annotated as in the
following example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1" emma:uninterpreted="true"/>
</emma:emma>
The notation for uninterpretable input can refer to any possible
stage of interpretation processing, including raw transcriptions.
For instance, if input speech cannot be correctly recognized or the
spoken input is not matched by a grammar (or by a language
constraint given to the recognition), it can be tagged as
emma:uninterpreted as in the following example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="raw"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr.xml"
emma:uninterpreted="true" emma:tokens="From Cambridge to London tomorrow"/>
</emma:emma>
Note that sometimes an input is classified as "uninterpreted"because its score falls below a confidence threshold set in the
processor. In this case it still may be useful for further stages
of processing to know what the highest scoring interpretation was,
even if that interpretation's confidence did not exceed the
threshold. If the interpretation is a raw speech recognition
result, an emma:tokens attribute can be used to
represent the best scoring result, as in the above example. If the
interpretation is a semantic result, the best scoring
interpretation can be included within the
emma:interpretation element, as
in the following example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1" emma:uninterpreted="true">
<source>philadelphia</source>
<destination>boston</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The emma:interpretation is empty only if the
emma:interpretation is annotated with either
emma:uninterpreted="true" or
emma:no-input="true".
4.2.5 Human language of input: emma:lang attribute
| Annotation |
emma:lang |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:language indicating the language for
the input. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, and application instance data. |
The emma:lang annotation is used to indicate the human
language for the input that it annotates. The values of the
emma:lang attribute are language identifiers as defined by [IETF RFC 1766]. For
example, emma:lang="fr" denotes French, and
emma:lang="en-US" denotes US English. emma:lang can
be applied to any emma:interpretation element. Its
annotative scope follows the annotative scope of these elements. In
contrast, the attribute xml:lang in XML 1.0 is used to
specify the language used in the contents and attribute values of
any element in an XML document. The attribute emma:lang must
be used if the xml:lang can no longer apply. For example,
the contents and attribute values of an element in the EMMA
document are from different languages, such as in the case where
the input language is in French, and the language of the annotated
attributes is in English.
The following example shows the use of emma:lang for
annotating an input interpretation.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:lang="fr">
<answer>arretez</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
In order handle inputs involving multiple languages, such as through code switching,
the emma:lang tag can contain several language identifiers
separated by spaces.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="int1"
emma:tokens="please stop arretez s'il vous plait"
emma:lang="en fr">
<command> CANCEL </command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.6 Reference to signal: emma:signal attribute
| Annotation |
emma:signal |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI referencing the input
signal. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence, application instance data. |
A URI reference to the signal that originated the input
recognition process may be represented in EMMA using the
emma:signal annotation.
Here is an example where the reference to the signal is applied
to the emma:interpretation element:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="intp1"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.bin">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.7 Media type: emma:media-type attribute
| Annotation |
emma:media-type |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string holding the MIME type
associated with the signal's data format. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group, emma:sequence, emma:endpoint, application instance data. |
The data format of the signal that originated the input may be
represented in EMMA using the emma:media-type annotation. An
initial set of MIME media types is defined by [RFC2046].
Here is an example where the media type for the ETSI ES 202 212
audio codec for Distributed Speech Recognition (DSR) is applied to
the emma:interpretation element. The example also specifies
an optional sampling rate of 8 kHz and maxptime of 40
milliseconds.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="intp1"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40">
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.8 Confidence scores: emma:confidence attribute
| Annotation |
emma:confidence |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:decimal in range 0.0 to 1.0,
indicating the processor's confidence in the result. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group,
emma:sequence, and application instance data. |
The confidence score in EMMA is used to indicate the quality of
the input, and it is the value assigned to emma:confidence
in the EMMA namespace. The confidence score is a number in the
range from 0.0 to 1.0 inclusive. A value of 0.0 indicates minimum
confidence, and a value of 1.0 indicates maximum confidence. Note
that emma:confidence should not be assumed to mean
only the confidence of the speech recognizer, but rather the
confidence of the whatever processor was responsible for creating
the EMMA result, based on whatever evidence it has. For a natural
language interpretation, for example, this might include semantic
heuristics in addition to speech recognition scores. Moreover, the
confidence score values do not have to be interpreted as
probabilities. In fact confidence score values are
platform-dependent, since their computation is likely to differ
between platforms and different EMMA processors. Confidence scores
are annotated explicitly in EMMA in order to provide this
information to the subsequent processes for multimodal interaction.
The example below illustrates how confidence scores are annotated
in EMMA.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="meaning1" emma:confidence="0.6">
<location>Boston</location>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="meaning2" emma:confidence="0.4">
<location> Austin </location>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
In addition to its use as an attribute on the EMMA interpretation and container
elements, the emma:confidence attribute can also be used to
assign confidences to elements in instance data in the application
namespace. This can be seen in the following example, where the
<destination> and <origin> elements have
confidences.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="meaning1" emma:confidence="0.6">
<destination emma:confidence="0.8"> Boston</destination>
<origin emma:confidence="0.6"> Austin </origin>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
Although in general instance data can be represented in XML
using a combination of elements and attributes in the application
namespace, EMMA does not provide a standard way to annotate
processors' confidences in attributes. Consequently, instance data
that is expected to be assigned confidences should be represented
using elements, as in the above example.
4.2.9 Input source: emma:source attribute
| Annotation |
emma:source |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI referencing the source of
input. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group ,
emma:sequence, and application instance data. |
The source of an interpreted input may be represented in EMMA as
a URI resource using the emma:source annotation.
Here is an example that shows different input sources for
different input interpretations.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example" xmlns:myapp="http://www.example.com/myapp">
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="intp1"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61">
<myapp:destination>Boston</myapp:destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="intp2"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-4024">
<myapp:destination>Austin</myapp:destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
4.2.10 Timestamps
The start and end times for input can be indicated using either
absolute timestamps or relative timestamps. Both are in
milliseconds for ease in processing timestamps. Note that the
absolute time may be conveniently determined using the ECMAScript
Date object's getTime() function.
4.2.10.1 Absolute timestamps: emma:start, emma:end attributes
| Annotation |
emma:start, emma:end |
| Definition |
Attributes indicating the absolute starting and ending times of
an input in terms of the number of milliseconds since 1 January
1970 00:00:00 GMT |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence,
emma:arc, emma:node,
application instance data |
Here is an example of a timestamp for an absolute time.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="int1"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542">
<destination>Chicago</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The emma:start and emma:end annotations on an
input can be identical, however the emma:end value cannot be
less than the emma:start value.
4.2.10.2 Relative timestamps:
emma:time-ref-uri, emma:time-ref-anchor-point,
emma:offset-to-start, emma:duration attributes
| Annotation |
emma:time-ref-uri |
| Definition |
Attribute of type xsd:anyURI indicating the URI used to
anchor the relative timestamp. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence,
emma:lattice, application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:time-ref-anchor-point |
| Definition |
Attribute with a value of start or end, defaulting to
start. It indicates whether to measure the time from the start or
end of the interval designated with emma:time-ref-uri. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of, emma:sequence,
emma:lattice, application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:offset-to-start |
| Definition |
Attribute with a signed integer value, defaulting to zero. It
specifies the offset in milliseconds for the start of input from
the anchor point designated with emma:reference-uri and
emma:anchor |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of, emma:sequence,
emma:arc, emma:node, application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:duration |
| Definition |
Attribute with an unsigned integer value, defaulting to zero.
It specifies the duration of the input in milliseconds. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of, emma:sequence,
emma:arc, application instance data |
Relative timestamps define the start of an input relative to the
start or end of a reference interval such as another input.
The reference interval is designated with
emma:time-ref-uri attribute. This can be combined with
emma:time-ref-anchor-point attribute to specify whether the anchor point is
the start or end of this interval. The start of an input relative
to this anchor point is then specified with
emma:offset-to-start attribute. Finally, the duration of an input can
be specified with emma:duration attribute. The emma:duration attribute
can be used independently of absolute or relative timestamps, e.g.
for annotation of speech corpora.
Here is an example where the referenced input is in the same
document:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:sequence>
<emma:interpretation id="int1">
<origin>Denver</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2"
emma:time-ref-uri="#int1"
emma:time-ref-anchor-point="start"
emma:offset-to-start="5000">
<destination>Chicago</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:sequence>
</emma:emma>
Note that the reference point refers to an input, but not
necessarily to a complete input. For example, if a speech
recognizer timestamps each word in an utterance, the anchor point
might refer to the timestamp for just one word.
The absolute and relative timestamps are not mutually exclusive;
that is, it is possible to have both relative and absolute
timestamp attributes on the same EMMA container element.
Timestamps of inputs collected by different devices will be
subject to variation if the times maintained by the devices are not
synchronized. This concern is outside of the scope of the EMMA
specification.
4.2.11 Medium, mode, and function of user inputs:
emma:medium, emma:mode,
emma:function, emma:verbal attributes
| Annotation |
emma:medium |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string constrained to values in the
set {acoustic, tactile, visual}. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, emma:endpoint, and application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:mode |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string with an open set of values including: {speech, dtmf_keypad, ink, gui, keys, video, photograph, ...}. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, emma:endpoint,and application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:function |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string constrained to values in the
open set {recording, transcription, dialog, verification,
...}. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, and application instance data |
| Annotation |
emma:verbal |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:boolean. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group, emma:one-of,
emma:sequence, and application instance data |
EMMA provides two properties for the annotation of input
modality. One indicating the broader medium or channel
(emma:medium) and another indicating the specific mode of
communication used on that channel (emma:mode).The input medium
is defined from the users perspective and indicates whether they
use their voice (acoustic), touch (tactile), or visual
appearance/motion (visual) as input. Tactile includes most
hand-on input device types such as pen, mouse, keyboard, and
touch screen. Visual is used for camera input.
emma:medium ::= [acoustic|tactile|visual]
The mode property provides the ability to distinguish between
different modes of communication that may be within a particular
medium. For example, in the tactile medium, modes include
electronic ink (ink), and pointing and clicking on a graphical user
interface (GUI).
emma:mode ::= [speech|dtmf_keypad|ink|gui|keys|video|photograph| ... ]
Orthogonal to the mode, user inputs can also be classified with
respect to their communicative function. This enables a simpler
mode classification.
emma:function ::= [recording|transcription|dialog|verification| ... ]
For example, speech can be used for recording (e.g. voicemail),
transcription (e.g. dictation), dialog (e.g interactive spoken
dialog systems), and verification (e.g. identifying users
through their voiceprints).
EMMA also supports an additional property emma:verbal which
distinguishes verbal use of an input mode from non-verbal. This can
be used to distinguish the use of electronic ink to convey
handwritten commands from the user of electronic ink for symbolic
gestures such as circles and arrows. Handwritten commands, such as
writing downtown in order to change a map display to show
the downtown are classified as verbal (emma:verbal="true"). Pen
gestures (arrows, lines, circles, etc), such as circling a
building, are classified as non-verbal dialog (emma:function="dialog"emma:verbal="false"). The use of handwritten words to transcribe an
email message is classified as transcription
(emma:function="transcription").
emma:verbal ::= [true|false]
Handwritten words and ink gestures are typically recognized
using different kinds of recognition components (handwriting
recognizer vs. gesture recognizer) and the verbal annotation will
be added by the recognition component which classifies the input.
The original input source, a pen in this case, will not be aware of
this difference. The input source identifier will tell you that the
input was from a pen of some kind but will not tell you if the mode
of input was handwriting (show downtown) or gesture (e.g.
circling an object or area).
Here is an example of the EMMA annotation for a pen input where
the user's ink is recognized as either a word ("Boston") or as an arrow:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of id="nbest1">
<emma:interpretation id="interp1"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true">
<location>Boston</location>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp2"
emma:confidence="0.4"
emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="false">
<direction>45</direction>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
Here is an example of the EMMA annotation for a spoken command
which is recognized as either "Boston" or "Austin":
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of>
<emma:interpretation id="interp1"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true">
<location>Boston</location>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="interp2"
emma:confidence="0.4"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true">
<location>Austin</location>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
The following table shows the relationship between the medium,
mode, and function properties and serves as an aid for classifying
inputs. For the dialog function it also shows some examples of the
classification of inputs as verbal vs. non-verbal.
| Medium |
Device |
Mode |
Function |
| recording |
dialog |
transcription |
verification |
| acoustic |
microphone |
speech |
audiofile (e.g. voicemail) |
spoken command / query / response (verbal = true) |
dictation |
speaker recognition |
| singing a note (verbal = false) |
| tactile |
keypad |
dtmf_keypad |
audiofile / character stream |
typed command / query / response (verbal = true) |
text entry (T9-tegic, word completion, or word
grammar) |
password / pin entry |
| command key "Press 9 for sales" (verbal = false) |
| keyboard |
dtmf_keypad |
character / key-code stream |
typed command / query / response (verbal = true) |
typing |
password / pin entry |
| command key "Press S for sales" (verbal = false) |
| pen |
ink |
trace, sketch |
handwritten command / query / response (verbal = true) |
handwritten text entry |
signature, handwriter recognition |
| gesture (e.g. circling building) (verbal = false) |
| gui |
N/A |
tapping on named button (verbal = true) |
soft keyboard |
password / pin entry |
| drag and drop, tapping on map (verbal = false) |
| mouse |
ink |
trace, sketch |
handwritten command / query / response (verbal = true) |
handwritten text entry |
N/A |
| gesture (e.g. circling building) (verbal = false) |
| gui |
N/A |
clicking named button (verbal = true) |
soft keyboard |
password / pin entry |
| drag and drop, clicking on map (verbal = false) |
| joystick |
ink |
trace,sketch |
gesture (e.g. circling building) (verbal = false) |
N/A |
N/A |
| gui |
N/A |
pointing, clicking button / menu (verbal = false) |
soft keyboard |
password / pin entry |
| visual |
page scanner |
photograph |
image |
handwritten command / query / response (verbal = true) |
optical character recognition, object/scene
recognition (markup, e.g. SVG) |
N/A |
| drawings and images (verbal = false) |
| still camera |
photograph |
image |
objects (verbal = false) |
visual object/scene recognition |
face id, retinal scan |
| video camera |
video |
movie |
sign language (verbal = true) |
audio/visual recognition |
face id, gait id, retinal scan |
| face / hand / arm / body gesture (e.g. pointing, facing)
(verbal = false) |
4.2.12 Support for composite multimodality:
emma:hook attribute
One of the most powerful aspects of multimodal interfaces is
their ability to provide support for user inputs which are
distributed over the available input modes. These composite
inputs are contributions made by the user within a single turn
which have component parts in different modes. For example, the
user might say "zoom in here" in the speech mode while drawing an
area on a graphical display in the ink mode. One of the central
motivating factors for this kind of input is that different kinds
of communicative content are best suited to different input modes.
In the example of a user drawing an area on a map and saying "zoom
in here", the zoom command is easiest to provide in speech but the
spatial information, the specific area, is easier to provide in
ink.
Enabling composite multimodality is critical in ensuring that
multimodal systems support more natural and effective interaction
for users. In order to support composite inputs, a multimodal
architecture must provide some kind of multimodal integration
mechanism. In the W3C
Multimodal Interaction Framework, multimodal integration can be
handled by an integration component which follows the application
of speech understanding and other kinds of interpretation
procedures for individual modes.
Given the broad range of different techniques being employed for
multimodal integration and the extent to which this is an ongoing
research problem, standardization of the specific method or
algorithm used for multimodal integration is not appropriate at
this time. In order to facilitate the development and
inter-operation of different multimodal integration mechanisms EMMA
provides markup language enabling application independent
specification of elements in the application markup where content
from another mode needs to be integrated. These representation
'hooks' can then be used by different kinds of multimodal
integration components and algorithms to drive the process of
multimodal integration. In the processing of a composite multimodal
input, the result of applying a mode-specific interpretation
component to each of the individual modes will be EMMA markup
describing the possible interpretation of that input. In the case of
speech, this markup can be assigned to speech through the
application of SRGS rules and their associated semantic
interpretation (SI) code. For some modes, some of those
interpretations may contain an application semantics which is
incomplete until content is added from another input mode. In the
example mentioned above, the speech command "zoom in here" is
incomplete until it is combined with the pen input of the user
circling an area.
4.2.12.1 Description of required annotation
| Annotation |
emma:hook |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string constrained to values in the
open set {speech, dtmf_keypad, ink, gui, keys, video, photograph,
...} or the wildcard any |
| Applies to |
Application instance data |
The attribute emma:hook is used to mark the elements in
the application semantics within an
emma:interpretation which must be integrated with
content from input in another mode. The emma:mode to be
integrated at that point in the application semantics is indicated
as the value of the emma:hook attribute. In the example
above, the annotation would be emma:hook="ink". The possible
values of emma:hook are the list of input modes that can be
values of emma:mode such as
speech, dtmf_keypad, ink, gui, keys.
In addition to these, the value of emma:hook can also be the
wildcard any indicating that the other content can come from
any source. The annotation emma:hook differs in semantics
from emma:mode as follows. Annotating an element in the
application semantics with emma:mode="ink" indicates that
that part of the semantics came from the ink mode.
Annotating an element in the application semantics with
emma:hook="ink" indicates that part of the semantics needs
to be integrated with content from the ink mode.
4.2.12.2 Simple example
To illustrate the use of emma:hook consider an example
composite input in which the user says "zoom in here" in the speech
input mode while drawing an area on a graphical display in the ink
input mode. One possible way to represent the application semantics
for "zoom in here" would be as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="speech">
<command>
<action>zoom</action>
<location emma:hook="ink">
<type>area</type>
</location>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
This representation would be assigned to the spoken input "zoom
in here" by a natural language understanding component. For
example, the semantics could be generated using the W3C Speech
Recognition Grammar Specification (SRGS)
using the Semantic Interpretation SI tags to
build the application semantics with the emma:hook
attribute. For more detailed explanation of this and an example see
Appendix: emma:hook and SRGS.
Note that the elements in the application markup here such as
<action>, <location>, and <points> are in no way
intended to be standardized. What is standardized is the use of
emma:hook="ink" to indicate where multimodal integration is
required. The action to be performed is indicated in an element
<action>. The location on which to perform the action is
indicated by the element <location>. The annotation
emma:hook="ink" on the <location> element indicates
that content needs to be added to this element through integration
with content from the ink input mode. In our example, the
interpretation of an area gesture could be represented as
follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="ink">
<location>
<type>area</type>
<points>42.1345 -37.128 42.1346 -37.120 ... </points>
</location>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
This representation could be generated by a pen modality
component performing gesture recognition and interpretation. The
input to the component would be an InkML specification of the ink
trace and the output would be the EMMA document above.
There are two components to the process of integrating these two
pieces of semantic markup. The first is to ensure that the two are
compatible; that is, that no semantic constraints are
violated. The second is to fuse the content from the two sources.
In our example, the <type>area</type> element is
intended to indicate that this speech command requires integration
with an area gesture rather than, for example, a line gesture,
which would have the subelement <type>line</type>. This
constraint needs to be enforced by whatever mechanism is
responsible for multimodal integration. In our example, the result
should be semantics of speech with the addition of new information
from the gesture, in this case the <points> element and its
contents:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="multimodal">
<command>
<action>zoom</action>
<location>
<type>area</type>
<points>42.1345 -37.128 42.1346 -37.120 ... </points>
</location>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.12.3 Possible integration algorithms
Many different techniques could be used for achieving this
integration of the semantic interpretation of the pen input, a
<location> element, with the corresponding <location>
element in the speech. The hook simply serves to indicate the
existence of this relationship.
One way to achieve both the compatibility checking and fusion of
content from the two modes is to use a well-defined general purpose
matching mechanism such unification. Graph unification is a mathematical
operation defined over directed acylic graphs which captures both
of the components of integration in a single operation: the
applications of the semantic constraints and the fusing of content.
One possible semantics for the emma:hook markup indicates
that content from the required mode needs to be unified with that
position in the application semantics. In order to unify, two
elements must not have any conflicting values for subelements or
attributes. This procedure can be defined recursively so that
elements within the subelements must also not clash and so on. The
result of unification is the union of all of the elements and
attributes of the two elements that are being unified.
In addition to the unification operation, in the resulting
emma:interpretation the emma:hook attribute
needs to be removed and the emma:mode attribute changed to
multimodal.
Instead of the unification operation, for a specific application
semantics, integration could be achieved using some other algorithm
or script. The benefit of using the unification semantics for
emma:hook is that it provides a general purpose mechanism
for checking the compatibility of elements and fusing them,
whatever the specific elements are in the application specific
semantic representation.
The benefit of using the emma:hook annotation for authors
is that it provides an application independent method for
indicating where integration with content from another mode is
required. If a general purpose integration mechanism is used, such
as the unification approach described above, authors should be able
to use the same integration mechanism for a range of different
applications without having to change the integration rules or
logic. For each application the speech grammar rules (SRGS) need to
assign emma:hook to the appropriate elements in the semantic
representation of the speech. The general purpose multimodal
integration mechanism will use the emma:hook annotations in
order to determine where to add in content from other modes.
Another benefit of the emma:hook mechanism is that it
facilitates interoperability among different multimodal integration
components, so long as they are all general purpose and utilize
emma:hook in order to determine where to integrate
content.
4.2.12.4 More detailed example
The following provides a more detailed example of the use of the
emma:hook annotation. In this example, spoken input is
combined with two gestures made use from ink. The semantic
representation assigned to the spoken input "send this file to
this" indicates two locations where content is required from ink
input using emma:hook="ink":
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation>
<command>
<action>send</action>
<arg1>
<object emma:hook="ink">
<type>file</type>
<number>1</number>
</object>
</arg1>
<arg2>
<object emma:hook="ink">
<number>1</number>
</object>
</arg2>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The user gesturing on the two locations on the display can be
represented using emma:sequence:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:sequence>
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="ink">
<object>
<type>file</type>
<number>1</number>
<id>test.pdf</id>
<object>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="ink">
<object>
<type>printer</type>
<number>1</number>
<id>lpt1</id>
<object>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:sequence>
</emma:emma>
A general purpose unification-based multimodal integration
algorithm could use the emma:hook annotation as follows. It
identifies the elements marked with emma:hook in document
order. For each of those in turn, it attempts to unify the element
with the corresponding element in order in the
emma:sequence. Since none of the subelements
conflict, the unification goes through and as a result, we have the
following EMMA for the composite result:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation>
<command>
<action>send</action>
<arg1>
<object>
<type>file</type>
<number>1</number>
<id>test.pdf</id>
</object>
</arg1>
<arg2>
<object>
<type>printer</type>
<number>1</number>
<id>lpt1</id>
</object>
</arg2>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
4.2.13 Cost: emma:cost attribute
| Annotation |
emma:cost |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:decimal in range 0.0 to 10000000,
indicating the processor's cost or weight associated with an input
or part of an input. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence, emma:arc, emma:node, and application
instance data. |
The cost annotation in EMMA is used to indicate the weight or
cost associated with an user's input or part of their input. The
most common use of emma:cost is for representing the costs
encoded on a lattice output from speech recognition or other
recognition or understanding processes. emma:cost can also
be used to indicate the total cost associated with particular
recognition results or semantic intepretations.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:one-of>
<emma:interpretation id="meaning1" emma:cost="1600">
<location>Boston</location>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="meaning2" emma:cost="400">
<location> Austin </location>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
4.2.14 Endpoint properties: emma:endpoint-role, emma:endpoint-address, emma:port-type, emma:port-num, emma:message-id, emma:service-name, emma:endpoint-pair-ref attributes
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint-role |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string constrained to values in the
set {source, sink, reply-to, router}. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint-address |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI that uniquely specifies the
network address of the emma:endpoint. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
| Annotation |
emma:port-type |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:QName that specifies the type of the
port. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
| Annotation |
emma:port-num |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:nonNegativeInteger that specifies the
port number. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint
|
| Annotation |
emma:message-id |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI that specifies the message ID
associated with the data. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
| Annotation |
emma:service-name |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:string that specifies the name of the
service. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint-pair-ref |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:anyURI that specifies the pairing
between sink and source endpoints. |
| Applies to |
emma:endpoint |
The emma:endpoint-role attribute is to specify the role
that the particular emma:endpoint performs in
multimodal interaction. The role value "sink" indicates that the
particular endpoint is the receiver of the input data. The role
value "source" indicates that the particular endpoint is the sender
of the input data. The role value "reply-to" indicates that the
particular emma:endpoint is the endpoint that the
reply should be sent to. The same emma:endpoint-address can
appear in multiple emma:endpoint; specifications,
provided that the same endpoint address is used to serve multiple
roles, e.g. sink, source, reply-to, router, etc., or associated
with multiple interpretations.
The emma:endpoint-address specifies the network address
of the emma:endpoint, and emma:port-type
specifies the port type of the emma:endpoint. The
emma:port-num annotates the port number of the endpoint
(e.g. the typical port number for an http endpoint is 80). The
emma:message-id annotates the message ID information
associated with the annotated input. This meta information is used
to establish and maintain the communication context for both
inbound processing and outbound operation. The service
specification of the emma:endpoint is annotated by
emma:service-name which contains the definition of the
service that the emma:endpoint performs. The matching
of the "sink" endpoint and its pairing "source" endpoint is
annotated by the emma:endpoint-pair-ref attribute. One sink
endpoint can link to multiple source endpoints through
emma:endpoint-pair-ref. Further boundling of the
emma:endpoint can be realized through the annotation
of emma:group [Ref: emma:group].
The following example illustrates the use of these attrubutes in
multimodal interactions where multiple modalities are used.
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example" xmlns: ex="http://www.example.com/emma/port">
<emma:endpoint-info id="audio-channel-1" >
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint1" emma:endpoint-role="sink"
emma:endpoint-address="135.61.71.103" emma:port-num="50204"
emma:port-type="rtp" emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint2"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint2" emma:endpoint-role="source"
emma:endpoint-address="136.62.72.104"
emma:port-num="50204" emma:port-type="rtp"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint1"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
</emma:endpoint-info>
<emma:endpoint-info id="ink-channel-1">
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint3" emma:endpoint-role="sink"
emma:endpoint-address="http://emma.example/sink"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint4"
emma:port-num="80" emma:port-type="http"
emma:message-id="uuid:2e5678"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="ink"/>
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint4" emma:endpoint-role="source"
emma:port-address="http://emma.example/source"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint3" emma:port-num="80"
emma:port-type="http" emma:message-id="uuid:2e5678"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="ink"/>
</emma:endpoint-info>
<emma:group>
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:endpoint-info-ref="audio-channel-1">
<destination>Chicago</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:endpoint-info-ref="ink-channel-1">
<location>
<type>area</type>
<points>34.13 -37.12 42.13 -37.12 ... </points>
</location>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:group>
</emma:emma>
4.2.14.1 Reference to
emma:endpoint-info element: emma:endpoint-info-ref attribute
| Annotation |
emma:endpoint-info-ref |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:IDREF referring to the id attribute of
an emma:endpoint-info element. |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence, and application instance data. |
The emma:endpoint-info-ref attribute associates the EMMA
result in the element to appears on with an emma:endpoint-info
element.
Example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example"
xmlns:ex="http://www.example.com/emma/port">
<emma:endpoint-info id="audio-channel-1" >
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint1" emma:endpoint-role="sink"
emma:endpoint-address="135.61.71.103"
emma:port-num="50204" emma:port-type="rtp"
emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint2"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
<emma:endpoint id="endpoint2" emma:endpoint-role="source"
emma:endpoint-address="136.62.72.104" emma:port-num="50204"
emma:port-type="rtp" emma:endpoint-pair-ref="endpoint1"
emma:media-type="audio/dsr-202212; rate:8000; maxptime:40"
emma:service-name="travel" emma:mode="speech">
<ex:app-protocol>SIP</ex:app-protocol>
</emma:endpoint>
</emma:endpoint-info>
<emma:one-of emma:endpoint-info-ref="audio-channel-1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542">
<destination>Chicago</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542">
<destination>Austin</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
4.2.15 Reference to emma:grammar element: emma:grammar-ref attribute
| Annotation |
emma:grammar-ref |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:IDREF referring to the
id attribute of an emma:grammar
element |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence. |
The emma:grammar-ref annotation associates the EMMA
result in the container element with an
emma:grammar element.
Example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:grammar id="gram1" href="someURI"/>
<emma:grammar id="gram2" href="anotherURI"/>
<emma:one-of id="r1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:grammar-ref="gram1">
<origin>Boston</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:grammar-ref="gram1">
<origin>Austin</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int3" emma:grammar-ref="gram2">
<command>help</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
4.2.16 Reference to emma:model element: emma:model-ref attribute
| Annotation |
emma:model-ref |
| Definition |
An attribute of type xsd:IDREF referring to the
id attribute of an emma:model
element |
| Applies to |
emma:interpretation, emma:group,
emma:one-of, emma:sequence, and
application instance data. |
The emma:model-ref annotation associates the EMMA
result in the container element with an
emma:model element.
Example:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:model id="model1" href="someURI"/>
<emma:model id="model2" href="anotherURI"/>
<emma:one-of id="r1">
<emma:interpretation id="int1" emma:model-ref="model1">
<origin>Boston</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int2" emma:model-ref="model1">
<origin>Austin</origin>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="int3" emma:model-ref="model2">
<command>help</command>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:one-of>
</emma:emma>
4.3. Scope of EMMA annotations
This section concerns the scope of EMMA annotations across
derivations of user input connected using the
emma:derived-from element (Section
4.1.2). The emma:derived-from element (Section 4.1.2) can be used to capture both sequential
and composite derivations. Sequential derivations involve
processing steps that do not involve multimodal integration, such
as applying natural language understanding and then reference
resolution to a speech transcription.
Annotation scope in sequential derivations is addressed in
Section 4.3.1. Composite derivations involve
combination of inputs from multiple different input modes. These
are addressed in Section 4.3.2 below. Note
that an EMMA derivation may include both sequential and composite
derivation steps. EMMA derivations describe only single turns of
user input and are not intended to describe a sequence of dialogue
turns.
In order to indicate whether an emma:derived-from;
element describes a sequential derivation step or a composite
derivation step, the emma:derived-from element; has an attribute
composite which has a boolean value. A composite
emma:derived-from; needs to be marked as
composite="true" while a sequential
emma:derived-from is marked as composite="false".
If this attribute is not specified the value is "false" by default.
4.3.1 Scope of EMMA annotations in sequential
derivation
This section concerns the scope of EMMA annotations in
sequential derivations. EMMA enables the annotation of whole
derivations of user input. For example an EMMA document could
contain emma:interpretation elements for the
transcription, interpretation, and reference resolution of a speech
input, utilizing the id values: raw, better,
and best respectively:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="raw"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr1.xml"/>>
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="better"
emma:process="http://example.com/mynlu1.xml">
<emma:derived-from resource="#raw" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="best"
emma:process="http://example.com/myrefresolution1.xml">
<emma:derived-from resource="#better" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
Each member of the derivation chain is linked to the previous
one by a derived-from element (Section 4.1.2), which has an attribute
resource that provides a pointer to the
emma:interpretation from which it is derived. The
emma:process annotation (Section
4.2.2) provides a pointer to the process used to for each stage
of the derivation.
The following EMMA example represents the same derivation as above
but with a more fully specified set of annotations:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="raw"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr1.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:tokens="from boston to denver tomorrow"
emma:lang="en-US">
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="better"
emma:process="http://example.com/mynlu1.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.8"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:tokens="from boston to denver tomorrow"
emma:lang="en-US">
<emma:derived-from resource="#raw" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="best"
emma:process="http://example.com/myrefresolution1.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.8"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:tokens="from boston to denver tomorrow"
emma:lang="en-US">
<emma:derived-from resource="#better" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
EMMA annotations on earlier stages of the derivation may still
be true of later stages of the derivation. Although this can be
captured in EMMA by repeating the annotations on each
emma:interpretation within the derivation, as in the example
above, there are two disadvantages of this approach to annotation.
First, the repetition of annotations makes the resulting EMMA
documents significantly more verbose. Second, EMMA processors used
for intermediate tasks such as natural language understanding and
reference resolution will need to read in all of the annotations
and write them all out again.
EMMA overcomes these problems by assuming that annotations on
earlier stages of a derivation automatically apply to later stages
of the derivation unless a new value is specified. Later stages of
the derivation essentially inherit annotations from earlier stages
in the derivation. For example, if there was an emma:source
annotation on the transcription (raw) it would also apply to
the later stages of the derivation such as the result of natural
language understanding (better) or reference resolution
(best).
Because of the assumption in EMMA that annotations have scope
over later stages of a sequential derivation, the example EMMA
document above can be equivalently represented as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="raw"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr1.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:tokens="from boston to denver tomorrow"
emma:lang="en-US">
<answer>From Boston to Denver tomorrow</answer>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="better"
emma:process="http://example.com/mynlu1.xml"
emma:confidence="0.8">
<emma:derived-from resource="#raw" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>tomorrow</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="best"
emma:process="http://example.com/myrefresolution1.xml">
<emma:derived-from resource="#better" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
The fully specified derivation illustrated above is equivalent
to the reduced form derivation following it where only annotations
with new values are specified at each stage. These two EMMA
documents should yield the same result when processed by an EMMA
processor.
The emma:confidence annotation is respecified on the
better interpretation. This indicates the confidence score
for natural language understanding, whereas emma:confidence
on the raw interpretation indicates the speech recognition
confidence score.
In order to determine the full set of annotations that apply to
an emma:interpretation element an EMMA processor or
script needs to access the annotations directly on that element and
for any that are not specified follow the reference in the
resource attribute of the emma:derived-from
element to add in annotations from earlier stages of the
derivation.
The EMMA annotations break down into three groups with respect to
their scope in sequential derivations. One group of annotations
always hold true for all members of a sequential derivation. A
second group are always respecified on each stage of the
derivation. A third group may or may not be respecified.
Scope of Annotations in Sequential Derivations
| Classification |
Annotation |
| Applies to whole derivation |
emma:signal |
emma:source |
emma:medium |
emma:mode |
emma:function |
emma:verbal |
emma:lang |
emma:tokens |
emma:start |
emma:end |
emma:time-ref-uri |
emma:time-ref-anchor-point |
emma:offset-to-start |
emma:duration |
| Specified at each stage of derivation |
emma:derived-from |
emma:process |
| May be respecified |
emma:confidence |
emma:cost |
emma:grammar-ref |
emma:model-ref |
emma:no-input |
emma:uninterpreted |
One potential problem with this annotation scoping mechanism is
that earlier annotations could be lost if earlier stages of a
derivation were dropped in order to reduce message size. This
problem can be overcome by considering annotation scope at the
point where earlier derivation stages are discarded and populating
the final interpretation in the derivation with all of the
annotations which it could inherit. For example, if the raw
and better stages were dropped the resulting EMMA document
would be:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:interpretation id="best"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:process="http://example.com/myrefresolution1.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.8"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:tokens="from boston to denver tomorrow"
emma:lang="en-US">
<emma:derived-from resource="#better" composite="false"/>
<origin>Boston</origin>
<destination>Denver</destination>
<date>03152003</date>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
If emma:one-ofappears with another emma:one-of
then annotations on the parent emma:one-of are assumed to apply to the
children of the child emma:one-of.
Unlike emma:one-of, annotations on an emma:group or
emma:sequence element are not assumed to apply to the children of the
emma:group or emma:sequence element.
4.3.2 Scope of EMMA annotations in composite derivations
In addition to representing sequential derivations, the EMMA
emma:derived-from element can also be used to
capture composite derivations. Composite derivations involve
combination of inputs from different modes. In the following
composite derivation example the user said "destination" and
circled Boston on a map:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="speech1"
emma:start="1087995962542"
emma:end="1087995964542"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:lang="en-US"
emma:tokens="destination">
<rawinput>destination</rawinput>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="pen1"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:process="http://example.com/mygesturereco.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/pen/wacom123"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/ink5.inkml"
emma:confidence="0.5"
emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="false">
<rawinput>Boston</rawinput>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="multimodal1"
emma:process="http://example.com/myintegrator.xml">
<emma:derived-from resource="#speech1" composite="true"/>
<emma:derived-from resource="#pen1" composite="true"/>
<destination>Boston</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
In this example, annotations on the multimodal interpretation
indicate the process used for the integration and there are two
emma:derived-from elements, one pointing to the
speech and one pointing to the pen gesture.
In EMMA, while annotations are assumed to have scope over later
stages in sequential derivation, they are not assumed to have scope
over compositional derivation steps. Annotations do not have scope
over composition derivation steps because the combining inputs
often have different values of a given annotation, as in the
annotations: emma:signal, emma:source,
emma:confidence, emma:start, and
emma:end. For some of these annotations, no single
value can be determined for the multimodal intepretation, for
example, emma:signal and emma:source. For others a
single value may be computed for the multimodal interpretation, but
it may involve more than simple inheritance. For example, the value
of emma:start for the multimodal interpretation
should be the earlier of the two time values from the two combining
inputs. In the above example:
emma:start="1087995961542". For
emma:end it should be the later of the two values on
the combining inputs: emma:end="1087995964542". In
the case of emma:confidence, the value for the composite is
result of a numerical function defined by the author of the
multimodal integration component or script. In the case of other
annotations such as emma:verbal, if either of the inputs has
the value true then the multimodal interpretation is
emma:verbal="true". In other words the annotation for the
composite input is the result of an inclusive OR of the boolean
values of the annotations on the inputs.
If an annotation is only specified in one of the combining
inputs then it can be assumed to apply to the multimodal
interpretation of the composite input. For example,
emma:lang="en-US" is only specified for the speech
input.
Given the complexity of annotation scope across composite
derivation steps, EMMA does not require any annotations to have
scope over composite derivation steps. However, guidance is
provided here for authors of multimodal integration components as
to how EMMA annotations should be handled in composite derivations.
The following table breaks down EMMA annotations in categories
depending on their behavior in composite derivations.
The general principle for combination of timestamps from combining inputs is
that the timestamp assigned to the combination of the inputs should be the
minimum interval which contains the intervals indicated by the timestamps
on the combining inputs. This is straightforward for absolute timestamps and more
complex for relative timestamps as indicated below.
Treatment of Annotations in Composite
Derivations
| Classification |
Annotation |
Function for value |
| 1. Always has different values |
emma:signal |
'multiple' |
emma:source |
emma:tokens |
emma:process |
New value(s) describing composite integration |
emma:derived-from |
| 2. Sometimes has different values |
emma:medium |
Common value or 'multiple' if they conflict |
emma:mode |
emma:lang |
emma:model |
| 3. Function combines values |
emma:start |
The earlier of the two start timestamps (standard) |
emma:end |
The later of the two end timestamps (standard) |
emma:time-ref-uri |
If the reference interval URI is the same for both inputs
then it should be the same for the composite input. If it is not
the same then relative timestamps will have to be resolved to
absolute timestamps in order to determine the combined timestamp.
. |
emma:time-ref-anchor-point |
If the the anchor value is the same for both inputs
then it should be the same for the composite input. If it is not
the same then relative timestamps will have to be resolved to
absolute timestamps in order to determine the combined timestamp. |
emma:offset-to-start |
Given that the emma:time-ref-uri
and emma:time-ref-anchor-point are the
same for both combining inputs, then the
emma:offset-to-start for the combination
should be the lesser of the two. If they are not
the same then relative timestamps will have to be resolved to
absolute timestamps in order to determine the combined timestamp. |
emma:duration |
Given that the emma:time-ref-uri
and emma:time-ref-anchor-point are the
same for both combining inputs, then the emma:duration
is calculated as follows. Add together the emma:offset-to-start
and emma:duration for each of the inputs. Take whichever of
these is greater and subtract from it the lesser of the emma:offset-to-start
values in order to determine the combined duration.
If emma:time-ref-uri and emma:time-ref-anchor-point are not
the same then relative timestamps will have to be resolved to
absolute timestamps in order to determine the combined timestamp.
|
emma:confidence |
combination of confidence scores (author-defined) |
emma:cost |
combination of costs (author-defined) |
emma:function |
some functions are dominant (e.g. 'dialog') (standard) |
emma:verbal |
inclusive OR of values (standard) |
| 4. Not integrated |
emma:uninterpreted |
Not applicable |
emma:no-input |
When a multimodal integration component generates the EMMA
document for composite intepretation, each of these sets of EMMA
annotations should be handled as indicated below.
1. Always has different values: The value of the
annotation on the multimodal interpretation should be
multiple indicating the presence of the conflict. In the
case of emma:process and emma:derived-from,
there will be new value(s) describing the integration process and
references to the combined inputs.
2. Sometimes has different values: If the values of an
annotation are the same for the combined inputs then that value
should be used in the annotation on the composite. If they are not
the same then the annotation value on the multimodal interpretation
should be multiple indicating the presence of the conflict.
If an annotation only appears on one of the inputs, then the value
for the input that has the annotation should be used for the
composite.
3. Function combines values: The values should be
combined in accordance with the specific function require for that
annotation. For some annotations the combination function is
standard; e.g. earliest value for emma:start, latest value
for emma:end, inclusive OR for emma:verbal. For
others, such as emma:confidence there is no standard
function and the function used will be defined by the application
developer.
4. Not integrated: Inputs with these annotations will not
be part of composite inputs and so they will not need to be
annotated in composite interpretations.
For 1. and 2. above, conflicts are indicated on the annotations
on the composite using the value multiple. If the values of
the annotations on the combining inputs are needed then they can be
accessed through the pointers in the resource attributes in
the emma:derived-from elements. However if the early
stages of the derivation have been dropped or are only remotely
accessible this may not be feasible. Unlike the sequential
derivation case, since the values may clash, the problem cannot be
avoided by fully instantiating the
emma:interpretation at the end of the derivation
chain.
In order to address this problem, values of conflicting
annotations must be indicated directly on the
emma:derived-from element. There will be one
emma:derived-from element for each combining input,
providing a place holder for annotations with conflicting
values.
The fully specified EMMA document for the composite input
described above is as follows:
<emma:emma version="1.0"
xmlns:emma:="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma
http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma10.xsd"
xmlns="http://www.example.com/example">
<emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="speech1"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:process="http://example.com/myasr.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:confidence="0.6"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:lang="en-US"
emma:tokens="destination">
<rawinput>destination</rawinput>
</emma:interpretation>
<emma:interpretation id="pen1"
emma:start="1087995961542"
emma:end="1087995963542"
emma:process="http://example.com/mygesturereco.xml"
emma:source="http://example.com/pen/wacom123"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/ink5.inkml"
emma:confidence="0.5"
emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="false">
<rawinput>Boston</rawinput>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:derivation>
<emma:interpretation id="multimodal1"
emma:source="multiple"
emma:signal="multiple"
emma:confidence="0.3"
emma:medium="multiple"
emma:mode="multiple"
emma:function="dialog"
emma:verbal="true"
emma:lang="en-US"
emma:tokens="destination">
<emma:derived-from resource="#speech1" composite="true"
emma:source="http://example.com/microphone/NC-61"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/sg23.wav"
emma:medium="acoustic"
emma:mode="speech"/>
<emma:derived-from resource="#pen1" emma:omposite="true"
emma:source="http://example.com/pen/wacom123"
emma:signal="http://example.com/signals/ink5.inkml"
emma:medium="tactile"
emma:mode="ink"/>
<destination>Boston</destination>
</emma:interpretation>
</emma:emma>
In this example, the annotations for emma:source,
emma:signal, emma:medium, and emma:mode all
have conflicting values on the inputs (#speech1and
#pen1) and are marked as multiple on the composite
interpretation (#multimodal1). The emma:lang and
emma:tokens are only specified on the speech
(#speech1) and therefore are inherited by the composite
interpretation (#multimodal1). The emma:start
and emma:end annotations are combined by standard
functions yielding the earliest and latest time values respectively
on #multimodal1. The emma:verbal annotation and
emma:function annotations are determined by standard
combination functions. Since the emma:verbal annotation is
true on the speech (#speech1)and false on
the pen (#pen1), the annotation on the composite
interpretation is true. Since both the speech and pen have
emma:function="dialog", the composite is annotated as
emma:function="dialog". The emma:confidence
annotation on the composite is determined by a non-standard
function defined by the author of the integration component. In
this case the function is multiplication and the resulting
annotation is emma:confidence="0.3".
In implementing an EMMA processor for composite input, the EMMA
annotations for timestamps, emma:function and
emma:verbal on the EMMA document representing the composite
input should be handled as indicated in the table above. This is a
constraint on documents representing composite derivation in
EMMA.
Appendices
Appendix A. XML schema
This section is Normative. The XML Schema definition for EMMA
markup is located at URI.
This section defines the formal syntax for EMMA documents in
terms of a normative XML Schema.
This schema is also available as http://www.w3.org/TR/emma/emma.xsd.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
elementFormDefault="unqualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
xmlns:emma="http://www.w3.org/2003/04/emma"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
EMMA 1.0 schema (20050830)
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
Copyright 1998-2005 W3C (MIT, ERCIM, Keio),
All Rights Reserved. Permission to use, copy,
modify and distribute the EMMA schema and its
accompanying documentation for any purpose and
without fee is hereby granted in perpetuity,
provided that the above copyright notice and this
paragraph appear in all copies. The copyright
holders make no representation about the suitability
of the schema for any purpose. It is provided
"as is" without expressed or implied warranty.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
EMMA element reference annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="grammar-ref" type="xs:IDREF"/>
<xs:attribute name="model-ref" type="xs:IDREF"/>
<xs:attribute name="endpoint-info-ref" type="xs:IDREF"/>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
endpoint annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="endpoint-pair-ref" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="service-name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="message-id" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="port-num" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger"/>
<xs:attribute name="port-type" type="xs:QName"/>
<xs:attribute name="endpoint-address" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="endpoint-role">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:NMTOKEN">
<xs:enumeration value="source"/>
<xs:enumeration value="sink"/>
<xs:enumeration value="reply-to"/>
<xs:enumeration value="router"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
cost annotation
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="cost">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:decimal">
<xs:minInclusive value="0.0"/>
<xs:maxInclusive value="10000000"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
hook annotation for composite integration
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="hook" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
medium, mode, and function annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="verbal" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="function" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="mode" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="medium">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:NMTOKEN">
<xs:enumeration value="acoustic"/>
<xs:enumeration value="tactile"/>
<xs:enumeration value="visual"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
timestamp annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="duration" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger" default="0"/>
<xs:attribute name="offset-to-start" type="xs:integer" default="0"/>
<xs:attribute name="time-ref-anchor-point" default="start">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:NMTOKEN">
<xs:enumeration value="start"/>
<xs:enumeration value="end"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="time-ref-uri" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="start" type="xs:unsignedLong"/>
<xs:attribute name="end" type="xs:unsignedLong"/>
<xs:attribute name="source" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="confidence">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:decimal">
<xs:minInclusive value="0.0"/>
<xs:maxInclusive value="1.0"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="media-type" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="signal" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="lang" type="xs:language"/>
<xs:attribute name="uninterpreted" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="no-input" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="process" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="tokens" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
endpoint definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType name="endpoint">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:endpoint-role"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:endpoint-address"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:message-id"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:port-num"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:port-type"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:endpoint-pair-ref"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:service-name"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:media-type"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:medium"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:mode"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
endpoint-info definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType name="endpoint-info">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:endpoint"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
info definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType name="info">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
grammar definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="grammar.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="href" type="xs:anyURI" use="required"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="grammar">
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:grammar.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
derivation definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType name="derivation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:sequence"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:group"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
derived-from definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="derived-from.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="resource" type="xs:anyURI" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="composite" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="derived-from">
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:derived-from.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
model definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="model.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:anyURI"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="model">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:model.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
literal definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType name="literal" mixed="true"/>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
lattice definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="node.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="node-number" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:end"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:offset-to-start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:confidence"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:cost"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="node">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:node.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:attributeGroup name="arc.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="from" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="to" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:end"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:offset-to-start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:duration"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:confidence"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:cost"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:lang"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:medium"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:mode"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:source"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="arc" mixed="true">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:arc.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:attributeGroup name="lattice.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="initial" type="xs:nonNegativeInteger" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="final" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:list itemType="xs:nonNegativeInteger"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:time-ref-uri"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:time-ref-anchor-point"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="lattice">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:arc"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:node"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:lattice.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
group annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="group.attribs">
<xs:attribute ref="emma:tokens"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:process"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:lang"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:signal"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:media-type"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:confidence"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:source"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:end"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:time-ref-uri"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:time-ref-anchor-point"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:offset-to-start"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:duration"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:medium"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:mode"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:function"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:verbal"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:cost"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:grammar-ref"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:endpoint-info-ref"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:model-ref"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
sequence definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:group name="sequence.class">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:derived-from"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:group"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:sequence"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="sequence">
<xs:group ref="emma:sequence.class"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:group.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
group-info definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="group-info.attribs">
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:anyURI"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:complexType name="group-info">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:group-info.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
group definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:group name="group.class">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:group-info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:derived-from"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:group"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:sequence"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="group">
<xs:group ref="emma:group.class"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:group.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
one-of definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:group name="one-of.class">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:derived-from"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
<xs:element ref="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:group"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:sequence"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="one-of">
<xs:group ref="emma:one-of.class"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:group.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
interpretation definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
interpretation annotations
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attributeGroup name="interpretation.attribs">
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:group.attribs"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:no-input"/>
<xs:attribute ref="emma:uninterpreted"/>
</xs:attributeGroup>
<xs:group name="interpretation.class">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:derived-from"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:lattice"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:literal"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other" processContents="lax" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="interpretation">
<xs:group ref="emma:interpretation.class"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:ID" use="required"/>
<xs:attributeGroup ref="emma:interpretation.attribs"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
emma definition
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:group name="emma.class">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
emma content model
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:derivation"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:grammar"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:model"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:endpoint-info"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:group"/>
<xs:element ref="emma:sequence"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="emma">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
emma content model and root attributes
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:group ref="emma:emma.class"/>
<xs:attribute name="version" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>
EMMA elements
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:element name="endpoint" type="emma:endpoint"/>
<xs:element name="endpoint-info" type="emma:endpoint-info"/>
<xs:element name="info" type="emma:info"/>
<xs:element name="grammar" type="emma:grammar"/>
<xs:element name="derivation" type="emma:derivation"/>
<xs:element name="derived-from" type="emma:derived-from"/>
<xs:element name="model" type="emma:model"/>
<xs:element name="literal" type="emma:literal"/>
<xs:element name="node" type="emma:node"/>
<xs:element name="arc" type="emma:arc"/>
<xs:element name="lattice" type="emma:lattice"/>
<xs:element name="sequence" type="emma:sequence"/>
<xs:element name="group-info" type="emma:group-info"/>
<xs:element name="group" type="emma:group"/>
<xs:element name="one-of" type="emma:one-of"/>
<xs:element name="interpretation" type="emma:interpretation"/>
<xs:element name="emma" type="emma:emma"/>
</xs:schema>
Leading and trailing spaces in utterances are not significant.
This will be defined in the Schema by specifying
"xml:space=default".
Appendix B. MIME type
This appendix registers a new MIME media type,
"application/emma+xml".
- MIME media type name:
-
application
- MIME subtype name:
-
emma+xml
- Required parameters:
-
None.
- Optional parameters:
-
charset-
This parameter has identical semantics to the
charset parameter of the
application/xml media type as specified in
[RFC3023].
- Encoding considerations:
-
By virtue of EMMA content being XML, it has the same
considerations when sent as "application/emma+xml"as does XML. See RFC 3023, section 3.2.
- Security considerations:
-
Several features of EMMA may cause arbitrary URIs to be
dereferenced. In this case, the security issues of RFC1738,
section 6, should be considered, see [RFC1738].
In addition, because of the extensibility features for EMMA,
it is possible that "application/emma+xml" may
describe content that has security implications beyond those
described here. However, if the processor follows only the
normative semantics of this specification, this content will be
ignored. Only in the case where the processor recognizes and
processes the additional content, or where further processing of
that content is dispatched to other processors, would security
issues potentially arise. And in that case, they would fall
outside the domain of this registration document.
- Interoperability considerations:
-
This specification describes processing semantics that dictate
behavior that must be followed when dealing with, among other
things, unrecognized elements.
Because EMMA is extensible, conformant
"application/emma+xml" processors can expect that
content received is well-formed XML, but it cannot be guaranteed
that the content is valid EMMA or that the processor will
recognize all of the elements and attributes in the document.
- Published specification:
-
This media type registration is for EMMA documents as
described by this specification.
- Additional information:
-
- Magic number(s):
-
There is no single initial octet sequence that is always
present in EMMA documents.
- File extension(s):
-
EMMA documents are most often identified with the
extensions ".emma".
- Macintosh File Type Code(s):
-
TEXT
- Person & email address to contact for further
information:
-
Dave Raggett, <dsr@w3.org>.
- Intended usage:
-
COMMON
- Author/Change controller:
-
The EMMA specification is a work product of the World Wide
Web Consortium's Multimodal Interaction Working Group. The W3C
has change control over these specifications.
Appendix C. emma:hook and SRGS
One way to build an EMMA representation of a spoken input such
as "zoom in here" is to use grammar rules in the W3C Speech
Recognition Grammar Specification [SRGS]
using using the Semantic Interpretation SI tags to
build the application semantics with the emma:hook
attribute. In this approach ECMAscript is is specified in order to
build up an object representing the semantics. The resulting
ECMAscript object is then translated to XML.
For our example case of "zoom in here". The following SRGS
rule could be used. The SI specification [SI] provides a reserved
property _nsprefix for indicating the namespace to be used
with an attribute.
<rule id="zoom">
zoom in here
<tag>
$.command = new Object();
$.command.action = "zoom";
$.command.location = new Object();
$.command.location._attributes = new Object();
$.command.location._attributes.hook = new Object();
$.command.location._attributes.hook._nsprefix = "emma";
$.command.location._attributes.hook._value = "ink";
$.command.location.type = "area";
</tag>
</rule>
Application of this rule will result in the following ECMAscript
object being built.
command: {
action: "zoom"
location: {
_attributes: {
hook: {
_nsprefix: "emma"
_value: "ink"
}
}
type: "area"
}
}
SI processing in an XML environment would generate the following
document:
<command>
<action>zoom</action>
<location emma:hook="ink">
<type>area</type>
</location>
</command>
This XML fragment might then appear within an EMMA document as
follows:
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="speech">
<command>
<action>zoom</action>
<location emma:hook="ink">
<type>area</type>
</location>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
The emma:hook annotation indicates that this speech input
needs to be combined with ink input such as the following:
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="ink">
<location>
<type>area</type>
<points>42.1345 -37.128 42.1346 -37.120 ... </points>
</location>
</emma:interpretation>
This will result in the following EMMA document for the combined
speech and pen multimodal input.
<emma:interpretation emma:mode="multimodal">
<command>
<action>zoom</action>
<location>
<type>area</type>
<points>42.1345 -37.128 42.1346 -37.120 ... </points>
</location>
</command>
</emma:interpretation>
Appendix D. EMMA event interface
The W3C Document Object Model [DOM] defines
platform and language neutral interfaces that gives programs and
scripts the means to dynamically access and update the content,
structure and style of documents. DOM Events define a generic
event system which allows registration of event handlers,
describes event flow through a tree structure, and provides basic
contextual information for each event.
This section of the EMMA specification extends the DOM Event
interface for use with events that describe interpreted user
input in terms of a DOM Node for an EMMA document.
// File: emma.idl
#ifndef _EMMA_IDL_
#define _EMMA_IDL_
#include "dom.idl"#include "views.idl"#include "events.idl"
#pragma prefix "dom.w3c.org"module emma
{
typedef dom::DOMString DOMString;
typedef dom::Node Node;
interface EMMAEvent : events::UIEvent {
readonly attribute dom::Node node;
void initEMMAEvent(in DOMString typeArg,
in boolean canBubbleArg,
in boolean cancelableArg,
in Node node);
};
};
#endif // _EMMA_IDL_
Appendix E. References
E.1 Normative references
- RFC1738
- T. Berners-Lee et al. editors. Uniform
Resource Locators (URL). IETF RFC 1738.
- RFC1766
- H. Alvestrand. Tags for the Identification of Languages. IETF RFC 1766.
- RFC3023
- M. Murata et al. editors. XML Media
ypes. IETF RFC 3023.
- RFC2046
- N. Freed and N. Borenstein. editors.
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part Two: Media Types. IETF RFC 2046.
- SI
- Luc Van Tichelen, editor. Semantic
Interpretation for Speech Recognition, World Wide Web
Consortium, 2004
- SRGS
- Andrew Hunt, Scott McGlashan, editors. Speech Recognition Grammar
Specification Version 1.0, World Wide Web Consortium, 2004
- XML
- Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen, and Eve Maler, Francois Yergeau,
editors. Extensible Markup
Language (XML) 1.0 (Third Edition). World Wide Web Consortium,
2004.
- XMLNS
- Andrew Layman, Richard Tobin, Tim Bray, Dave Hollander,
editors, Namespaces in
XML 1.1, World Wide Web Consortium, 2004.
- XML Schema Structures
- Henry S. Thompson, David Beech, Murray Maloney, Noah
Mendelsohn, editors. XML Schema Part 1:
Structures Second Edition, World Wide Web Consortium, 2004.
- XML Schema Datatypes
- Paul V. Biron, Ashok Malhotra, editors.
XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes Second Edition, Section 3.2.17,
World Wide Web Consortium, 2004.
E.2 Informative references
- DOM
- Document Object
Model, World Wide Web Consortium, 2005.
- EMMA Requirements
- Stephane H. Maes and Stephen Potter, editors. Requirements for EMMA, World
Wide Web Consortium, 2003
- Graph Unification
- Bob Carpenter. 1992. The Logic of Typed Feature
Structures. Cambridge Tracts in Theoretical Computer Science
32. Cambridge
University Press.
- Kevin Knight. 1989. Unification: A Multidisciplinary
Survey ACM Computing Surveys, 21(1).
- MMI Framework
- James A. Larson, T.V. Raman and Dave Raggett, editors. W3C Multimodal Interaction
Framework, World Wide Web Consortium, 2003
- MMI Requirements
- Stephane H. Maes and Vijay Saraswat, editors. Multimodal Interaction
Requirements, World Wide Web Consortium, 2003
Appendix F. Changes since last draft
Since the publication of the last working draft, the EMMA specification has undergone
major restructuring and numerous editorial changes and corrections. Section 2.1 now provides a compact overview of the different kinds of EMMA elements and attributes. Structural elements and annotations are
described in Sections 3 and 4 respectively, and 4 is broken down into Annotation Elements (4.1) and
Annotation attributes (4.2). The section on the scope of EMMA annotations has been merged into Section 4 (4.3). The
appendices have also been reorganized. In addition
to numerous changes in presentation there have also been substantive changes in the content, the most
significant of which are itemized below:
- A new
emma:derivation element has been added which serves as a container for
EMMA markup describing earlier stages of the derivation. This simplifies processing by ensuring that the
top level emma:interpretation, emma:one-of, emma:group,
or emma:sequence contains the latest stage of processing.
- Tables defining elements throughout have been extended to provide detail on their
children, what they can be a child of, and what their required and optional attributes are.
- Definition of
emma:arc has been revised to allow for XML content to appear
within it.
- New terminology section has been added (1.2).
- New appendix on EMMA MIME type (Appendix B).
- New appendix on EMMA event interface (Appendix D).
- New section on conformance (2.4).
- Revision of annotation elements
emma:endpoint-info and emma:model so
that like emma:grammar they can only appear under emma:emma and are
associated by reference with the interpretations they apply to. New emma:model-ref attribute introduced
for associating interpretations with the appropriate emma:model.
- Added explanation in 4.1.2 showing how
emma:derived-from can be used with emma:one-of to provide either course or fine-grained annotation of derivation relations.
- Added new section 2.3 on when namespace prefixes should be used.
- Revised the attribute
emma:time-ref-anchor to emma:time-ref-anchor-point to avoid confusion with html anchors.
- Added new
emma:literal which serves as a wrapper for semantic values with no
internal structure.
- New specification added on how relative timestamps can be used with lattices (3.4.3).
Appendix G. Acknowledgements
The editors would like to recognize the contributions of the
following members of the W3C Multimodal Interaction Group
(listed in alphabetical order):
Paolo Baggia, Loquendo
Patrizio Bergallo, Loquendo
Daniel Burnett, Nuance Communications
Max Froumentin, W3C
Katriina Halonen, Nokia
Roberto Pieraccini, IBM
Stephen Potter, Microsoft
Yuan Shao, Canon

